Macrophage-Specific NLRC5 Protects From Cardiac Remodeling Through Interaction With HSPA8
- PMID: 37325412
- PMCID: PMC10264565
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2022.10.001
Macrophage-Specific NLRC5 Protects From Cardiac Remodeling Through Interaction With HSPA8
Abstract
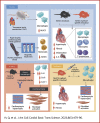
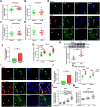
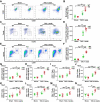
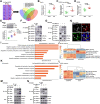
Macrophages regulate inflammation and the process of tissue repair. Therefore, a better understanding of macrophages in the pathogenesis of heart failure is needed. In patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, NLRC5 was significantly increased in circulating monocytes and cardiac macrophages. Myeloid-specific deletion of NLRC5 aggravated pressure overload-induced pathological cardiac remodeling and inflammation. Mechanistically, NLRC5 interacted with HSPA8 and suppressed NF-κB pathway in macrophages. The absence of NLRC5 in macrophages promoted the secretion of cytokines such as interleukin-6 (IL-6), which affected cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and cardiac fibroblast activation. Tocilizumab, an anti-IL-6 receptor antagonist, may be a novel therapeutic strategy for cardiac remodeling and chronic heart failure.
Keywords: NOD-like receptor; cardiac remodeling; heart failure; immunomodulatory therapy; macrophages.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China grants 81800424, 81900239, 81670746, 91939101, and 82070230, Clinical Research Plan of SHDC No. SHDC2020CR4019, and the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai No. 20ZR1435300. The authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures




References
-
- Heidenreich P.A., Bozkurt B., Aguilar D., et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022;79:e263–e421. - PubMed
-
- Ridker P.M., Devalaraja M., Baeres F.M.M., et al. IL-6 inhibition with ziltivekimab in patients at high atherosclerotic risk (RESCUE): a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2021;397:2060–2069. - PubMed
-
- Ridker P.M., Everett B.M., Thuren T., et al. Antiinflammatory therapy with canakinumab for atherosclerotic disease. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:1119–1131. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

