Platinum nanoparticles labelled with iodine-125 for combined "chemo-Auger electron" therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 37325536
- PMCID: PMC10262957
- DOI: 10.1039/d3na00165b
Platinum nanoparticles labelled with iodine-125 for combined "chemo-Auger electron" therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
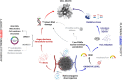
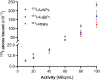
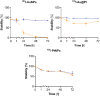
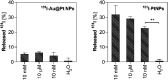
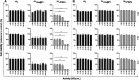
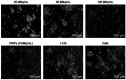
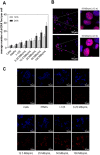
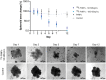
Convenient therapeutic protocols against hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) exhibit low treatment effectiveness, especially in the context of long-term effects, which is primarily related to late diagnosis and high tumor heterogeneity. Current trends in medicine concern combined therapy to achieve new powerful tools against the most aggressive diseases. When designing modern, multimodal therapeutics, it is necessary to look for alternative routes of specific drug delivery to the cell, its selective (with respect to the tumor) activity and multidirectional action, enhancing the therapeutic effect. Targeting the physiology of the tumor makes it possible to take advantage of certain characteristic properties of the tumor that differentiate it from other cells. In the present paper we designed for the first time iodine-125 labeled platinum nanoparticles for combined "chemo-Auger electron" therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. High selectivity achieved by targeting the tumor microenvironment of these cells was associated with effective radionuclide desorption in the presence of H2O2. The therapeutic effect was found to be correlated with cell damage at various molecular levels including DNA DSBs and was observed in a dose-dependent manner. A three-dimensional tumor spheroid revealed successful radioconjugate anticancer activity with a significant treatment response. A possible concept for clinical application after prior in vivo trials may be achieved via transarterial injection of micrometer range lipiodol emulsions with encapsulated 125I-NP. Ethiodized oil gives several advantages especially for HCC treatment; thus bearing in mind a suitable particle size for embolization, the obtained results highlight the exciting prospects for the development of PtNP-based combined therapy.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
109Pd/109mAg in-vivo generator in the form of nanoparticles for combined β- - Auger electron therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma.EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2024 Aug 13;9(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s41181-024-00293-9. EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2024. PMID: 39136900 Free PMC article.
-
Au@Pt Core-Shell Nanoparticle Bioconjugates for the Therapy of HER2+ Breast Cancer and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Model Studies on the Applicability of 193mPt and 195mPt Radionuclides in Auger Electron Therapy.Molecules. 2021 Apr 3;26(7):2051. doi: 10.3390/molecules26072051. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33916671 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Lipiodol as a drug-delivery system for transcatheter arterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma: a review.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2013 Dec;88(3):530-49. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2013.07.003. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2013. PMID: 23921081 Review.
-
Highly Tumor-Specific and Long-Acting Iodine-131 Microbeads for Enhanced Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Low-Dose Radio-Chemoembolization.ACS Nano. 2021 Feb 23;15(2):2933-2946. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c09122. Epub 2021 Feb 2. ACS Nano. 2021. PMID: 33529007
-
Radionuclide therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma.Ann Acad Med Singap. 2003 Jul;32(4):518-24. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2003. PMID: 12968558 Review.
Cited by
-
Developing a Tumor Microenvironment in Rotating Human Melanoma Cell Cultures: Study of a Novel Preclinical Model.ACS Omega. 2025 Jun 20;10(25):27288-27300. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c02682. eCollection 2025 Jul 1. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40621031 Free PMC article.
-
Application of radioactive iodine-125 microparticles in hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein embolus.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2024 Jul 27;16(7):2023-2030. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i7.2023. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2024. PMID: 39087134 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the history and trends of nanotechnology for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a bibliometric-based visual analysis.Discov Oncol. 2025 Apr 7;16(1):484. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02145-7. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40192866 Free PMC article.
-
109Pd/109mAg in-vivo generator in the form of nanoparticles for combined β- - Auger electron therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma.EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2024 Aug 13;9(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s41181-024-00293-9. EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2024. PMID: 39136900 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

