Non-natural amino acids into LfcinB-derived peptides: effect in their (i) proteolytic degradation and (ii) cytotoxic activity against cancer cells
- PMID: 37325596
- PMCID: PMC10265003
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.221493
Non-natural amino acids into LfcinB-derived peptides: effect in their (i) proteolytic degradation and (ii) cytotoxic activity against cancer cells
Abstract
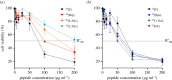
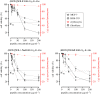
The dimeric peptide 26[F]: (RRWQWRFKKLG)2-K-Ahx has exhibited a potent cytotoxic effect against breast cancer cell lines, with position 26 (F) being the most relevant for anti-cancer activity. In this investigation, six analogues of the 26[F] peptide were synthesized in which the 26th position was replaced by non-natural hydrophobic amino acids, finding that some modifications increased the resistance to proteolytic degradation exerted by trypsin or pepsin. Additionally, these modifications increased the cytotoxic effect against breast cancer cells and generated cell death mediated by apoptosis pathways, activating caspases 8 and 9, and did not compromise the integrity of the cytoplasmic membrane. Finally, it was found that the modified peptides have a broad spectrum of action, since they also have a cytotoxic effect against the HeLa human cervical cancer cell line. Peptide 26[F] was inoculated in mice by ip administration and the lethal dose 50 (LD50) was between 70 and 140 mg kg-1. While for the 26[1-Nal]: (RRWQWR-1-Nal-KKLG)2-K-Ahx peptide, a dose-response test was performed, and the survival rate was 100%. These results suggested that these peptides are safe in this animal model and could be considered as promissory to develop a treatment against breast cancer.
Keywords: LfcinB-derived peptides; MCF-7 cells; cytotoxic activity; non-natural amino acids; proteolytic degradation.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ritchie H, Roser M. 2015 Cancer. Our World in Data. See https://ourworldindata.org/cancer.
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
