Multi-functional adaptor SKAP1: regulator of integrin activation, the stop-signal, and the proliferation of T cells
- PMID: 37325633
- PMCID: PMC10264576
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1192838
Multi-functional adaptor SKAP1: regulator of integrin activation, the stop-signal, and the proliferation of T cells
Abstract
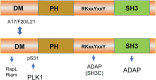
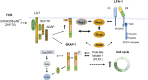
T-cell activation is a complex process involving a network of kinases and downstream molecular scaffolds or adaptors that integrate surface signals with effector functions. One key immune-specific adaptor is Src kinase-associated phosphoprotein 1 (SKAP1), which is also known as src kinase-associated protein of 55 kDa (SKAP55). This mini-review explains how SKAP1 plays multiple roles in regulating integrin activation, the "stop-signal", and the optimization of the cell cycling of proliferating T cells through interactions with various mediators, including the Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1). Ongoing research on SKAP1 and its binding partners will likely provide important insights into the regulation of immune function and have implications for the development of new treatments for disease states such as cancer and autoimmunity.
Keywords: SKAP1; T-cells; adaptor protein; integrin activation; signalling.
Copyright © 2023 Liu, Raab, Gui and Rudd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immune adaptor SKAP1 acts a scaffold for Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) for the optimal cell cycling of T-cells.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 18;9(1):10462. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45627-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31320682 Free PMC article.
-
Role of two modules controlling the interaction between SKAP1 and SRC kinases comparison with SKAP2 architecture and consequences for evolution.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 14;19(3):e0296230. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296230. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38483858 Free PMC article.
-
The N terminus of SKAP55 enables T cell adhesion to TCR and integrin ligands via distinct mechanisms.J Cell Biol. 2013 Dec 23;203(6):1021-41. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201305088. J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24368808 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin signalling and function in immune cells.Immunology. 2012 Apr;135(4):268-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03549.x. Immunology. 2012. PMID: 22211918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrin-regulated FAK-Src signaling in normal and cancer cells.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006 Oct;18(5):516-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2006.08.011. Epub 2006 Aug 17. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16919435 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamics of single-nuclei transcriptomic profiling of adipose tissue from diverse anatomical locations during mouse aging process.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 12;14(1):16093. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66918-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38997312 Free PMC article.
-
Pervasive nuclear envelope ruptures precede ECM signaling and disease onset without activating cGAS-STING in Lamin-cardiomyopathy mice.Cell Rep. 2024 Jun 25;43(6):114284. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114284. Epub 2024 May 29. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38814785 Free PMC article.
-
FYB1-targeted modulation of CAPG promotes AML progression.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Feb;480(2):985-999. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-04992-4. Epub 2024 May 3. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 38700746 Free PMC article.
-
Single cell analyses reveal the PD-1 blockade response-related immune features in hepatocellular carcinoma.Theranostics. 2024 Jun 1;14(9):3526-3547. doi: 10.7150/thno.95971. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38948071 Free PMC article.
-
Pervasive nuclear envelope ruptures precede ECM signaling and disease onset without activating cGAS-STING in Lamin-cardiomyopathy mice.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 18:2023.08.28.555134. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.28.555134. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cell Rep. 2024 Jun 25;43(6):114284. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114284. PMID: 37693381 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

