Vital roles of m5C RNA modification in cancer and immune cell biology
- PMID: 37325635
- PMCID: PMC10264696
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1207371
Vital roles of m5C RNA modification in cancer and immune cell biology
Abstract
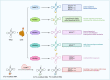
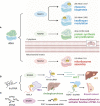
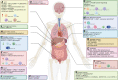
RNA modification plays an important role in epigenetics at the posttranscriptional level, and 5-methylcytosine (m5C) has attracted increasing attention in recent years due to the improvement in RNA m5C site detection methods. By influencing transcription, transportation and translation, m5C modification of mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, lncRNA and other RNAs has been proven to affect gene expression and metabolism and is associated with a wide range of diseases, including malignant cancers. RNA m5C modifications also substantially impact the tumor microenvironment (TME) by targeting different groups of immune cells, including B cells, T cells, macrophages, granulocytes, NK cells, dendritic cells and mast cells. Alterations in immune cell expression, infiltration and activation are highly linked to tumor malignancy and patient prognosis. This review provides a novel and holistic examination of m5C-mediated cancer development by examining the exact mechanisms underlying the oncogenicity of m5C RNA modification and summarizing the biological effects of m5C RNA modification on tumor cells as well as immune cells. Understanding methylation-related tumorigenesis can provide useful insights for the diagnosis as well as the treatment of cancer.
Keywords: RNA modification; cancer; cancer immunity; immune cells; m5C.
Copyright © 2023 Gu, Ma, Chen, Guan, Wang, Wu and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RNA m5C regulator-mediated modification patterns and the cross-talk between tumor microenvironment infiltration in gastric cancer.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 27;13:905057. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.905057. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36389669 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of m5C Methylation Regulatory Genes and Tumor Microenvironment in Prostate Cancer.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 10;13:914577. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.914577. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35757739 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of m5C RNA Modification Patterns in Biochemical Recurrence and Tumor Microenvironment Characterization of Prostate Adenocarcinoma.Front Immunol. 2022 May 4;13:869759. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.869759. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35603206 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the RNA m6A modification for cancer immunotherapy.Mol Cancer. 2022 Mar 16;21(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01558-0. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35296338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N6-Methyladenosine RNA Modification in the Tumor Immune Microenvironment: Novel Implications for Immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 9;12:773570. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.773570. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34956201 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MARCH8/NSUN6/ROS-mediated DNA damage positive feedback loop regulates cisplatin resistance in osteosarcoma.Cell Death Differ. 2025 Jul 19. doi: 10.1038/s41418-025-01544-1. Online ahead of print. Cell Death Differ. 2025. PMID: 40683951
-
m5c-iEnsem: 5-methylcytosine sites identification through ensemble models.Bioinformatics. 2022 Jan 1;41(1):btae722. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae722. Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 39657957 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting tRNA methyltransferases: from molecular mechanisms to drug discovery.Sci China Life Sci. 2025 Sep;68(9):2550-2567. doi: 10.1007/s11427-024-2886-2. Epub 2025 May 7. Sci China Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40347212 Review.
-
The roles and mechanisms of coding and noncoding RNA variations in cancer.Exp Mol Med. 2024 Sep;56(9):1909-1920. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01307-x. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Exp Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39218979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection, molecular function and mechanisms of m5C in cancer.Clin Transl Med. 2025 Mar;15(3):e70239. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70239. Clin Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40008496 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

