The Histone Methyltransferase SETDB2 Modulates Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinase-Matrix Metalloproteinase Activity During Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Development
- PMID: 37325923
- PMCID: PMC10526639
- DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000005963
The Histone Methyltransferase SETDB2 Modulates Tissue Inhibitors of Metalloproteinase-Matrix Metalloproteinase Activity During Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Development
Abstract
Objective: To determine macrophage-specific alterations in epigenetic enzyme function contributing to the development of abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs).
Background: AAA is a life-threatening disease, characterized by pathologic vascular remodeling driven by an imbalance of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs). Identifying mechanisms regulating macrophage-mediated extracellular matrix degradation is of critical importance to developing novel therapies.
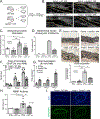
Methods: The role of SET Domain Bifurcated Histone Lysine Methyltransferase 2 (SETDB2) in AAA formation was examined in human aortic tissue samples by single-cell RNA sequencing and in a myeloid-specific SETDB2 deficient murine model induced by challenging mice with a combination of a high-fat diet and angiotensin II.
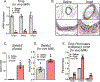
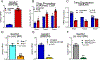
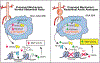
Results: Single-cell RNA sequencing of human AAA tissues identified SETDB2 was upregulated in aortic monocyte/macrophages and murine AAA models compared with controls. Mechanistically, interferon-β regulates SETDB2 expression through Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling, which trimethylates histone 3 lysine 9 on the TIMP1-3 gene promoters thereby suppressing TIMP1-3 transcription and leading to unregulated matrix metalloproteinase activity. Macrophage-specific knockout of SETDB2 ( Setdb2f/fLyz2Cre+ ) protected mice from AAA formation with suppression of vascular inflammation, macrophage infiltration, and elastin fragmentation. Genetic depletion of SETDB2 prevented AAA development due to the removal of the repressive histone 3 lysine 9 trimethylation mark on the TIMP1-3 gene promoter resulting in increased TIMP expression, decreased protease activity, and preserved aortic architecture. Lastly, inhibition of the Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of the transcription pathway with an FDA-approved inhibitor, Tofacitinib, limited SETDB2 expression in aortic macrophages.
Conclusions: These findings identify SETDB2 as a critical regulator of macrophage-mediated protease activity in AAAs and identify SETDB2 as a mechanistic target for the management of AAAs.
Copyright © 2023 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Myeloid Cells in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2025 May 22;27(1):57. doi: 10.1007/s11883-025-01302-1. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2025. PMID: 40402405 Review.
-
Disruption of PCSK9 Suppresses Inflammation and Attenuates Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Formation.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2025 Jan;45(1):e1-e14. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.123.320391. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2025. PMID: 39588646
-
Genetic analysis of polymorphisms in biologically relevant candidate genes in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysms.J Vasc Surg. 2005 Jun;41(6):1036-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2005.02.020. J Vasc Surg. 2005. PMID: 15944607 Free PMC article.
-
BAF60a Deficiency in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Prevents Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm by Reducing Inflammation and Extracellular Matrix Degradation.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020 Oct;40(10):2494-2507. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314955. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020. PMID: 32787523 Free PMC article.
-
The contribution of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors to the development, progression, and rupture of abdominal aortic aneurysms.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Sep 19;10:1248561. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1248561. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37799778 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic Role of SETDB2 in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: Linking Immune Infiltration, Cuproptosis, and Tumor Suppression.Cancer Manag Res. 2025 Mar 27;17:675-692. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S499771. eCollection 2025. Cancer Manag Res. 2025. PMID: 40166493 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophages in cardiovascular diseases: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 May 31;9(1):130. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01840-1. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38816371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles and mechanisms of histone methylation in vascular aging and related diseases.Clin Epigenetics. 2025 Feb 23;17(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13148-025-01842-y. Clin Epigenetics. 2025. PMID: 39988699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myeloid Cells in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2025 May 22;27(1):57. doi: 10.1007/s11883-025-01302-1. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2025. PMID: 40402405 Review.
-
Epigenetic alteration of smooth muscle cells regulates endothelin-dependent blood pressure and hypertensive arterial remodeling.J Clin Invest. 2025 Mar 27;135(11):e186146. doi: 10.1172/JCI186146. eCollection 2025 Jun 2. J Clin Invest. 2025. PMID: 40146226 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

