Assessment of inter-observer agreement among experienced and inexperienced observers and an automated device for dipstick urinalysis in dogs and cats
- PMID: 37326167
- PMCID: PMC10467455
- DOI: 10.1177/10406387231181579
Assessment of inter-observer agreement among experienced and inexperienced observers and an automated device for dipstick urinalysis in dogs and cats
Abstract
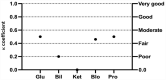
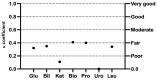
Standard visual urine dipstick analysis (UDA) is performed routinely in veterinary medicine; results can be influenced by both the operator and the method. We evaluated the agreement of results for canine and feline urine samples analyzed using a 10-patch dipstick (Multistix10SG; Siemens), both visually under double-anonymized conditions by students and a laboratory technician, and with an automated device (AD; Clinitek Status, Siemens). The mean concordance for semiquantitative urinalysis results between students and the technician and between students and the AD was fair (κ0.21-0.40) in dogs and cats; concordance was moderate between the technician and the AD (κ0.41-0.60) in dogs and good (κ0.61-0.80) in cats. For pH, the mean concordance between students and the technician and between the technician and the AD was good (ρ0.80-0.92) in dogs and cats; concordance was good between students and the AD (ρ0.80-0.92) in dogs and moderate (ρ0.59-0.79) in cats. Repeatability was higher (p < 0.001) for the technician and the AD than for a student. We found good agreement between UDA performed by an experienced operator and an AD in dogs and cats but found low reproducibility and low repeatability for urinalysis performed by an inexperienced operator.
Keywords: cats; dogs; urinalysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures





References
-
- Arnold JE, et al.. ASVCP guidelines: principles of quality assurance and standards for veterinary clinical pathology (v.3.0): developed by the American Society for Veterinary Clinical Pathology’s (ASVCP) Quality Assurance and Laboratory Standards (QALS) Committee. Vet Clin Pathol 2019;48:542–618. - PubMed
-
- Athanasiou LV, et al.. Comparison between the urine dipstick and the pH-meter to assess urine pH in sheep and dogs. Vet Clin Pathol 2018;47:284–288. - PubMed
-
- Bauer N, et al.. Evaluation the Clinitek Status automated dipstick analysis device for semiquantitative testing of canine urine. Res Vet Sci 2008;85:467–472. - PubMed
-
- Brereton DM, et al.. Timing of urinalysis reactions when reagent strips are used. Clin Chem 1978;24:1420–1421. - PubMed
-
- da Fonseca Ferreira M, et al.. Urine dipstick precision with standard visual and automated methods within a small animal teaching hospital. Vet Rec 2018;183:415. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

