Guidance on treatment endpoints and study design for clinical trials aiming to achieve cure in chronic hepatitis B and D: Report from the 2022 AASLD-EASL HBV-HDV Treatment Endpoints Conference
- PMID: 37326326
- PMCID: PMC12373085
- DOI: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000431
Guidance on treatment endpoints and study design for clinical trials aiming to achieve cure in chronic hepatitis B and D: Report from the 2022 AASLD-EASL HBV-HDV Treatment Endpoints Conference
Abstract
Representatives from academia, industry, regulatory agencies, and patient advocacy groups convened under the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) and the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL) in June 2022 with the primary goal of achieving consensus on chronic HBV and HDV treatment endpoints to guide clinical trials aiming to "cure" HBV and HDV. Conference participants reached an agreement on some key points. The preferred primary endpoint for phase II/III trials evaluating finite treatments for chronic hepatitis B (CHB) is a "functional" cure, defined as sustained HBsAg loss and HBV DNA less than the lower limit of quantitation (LLOQ) 24 weeks off-treatment. An alternate endpoint would be "partial cure" defined as sustained HBsAg level < 100 IU/mL and HBV DNA < LLOQ 24 weeks off-treatment. Clinical trials should initially focus on patients with HBeAg positive or negative CHB, who are treatment-naive or virally suppressed on nucleos(t)ide analogs. Hepatitis flares may occur during curative therapy and should be promptly investigated and outcomes reported. HBsAg loss would be the preferred endpoint for chronic hepatitis D, but HDV RNA < LLOQ 24 weeks off-treatment is a suitable alternate primary endpoint of phase II/III trials assessing finite strategies. For trials assessing maintenance therapy, the primary endpoint should be HDV RNA < LLOQ assessed at on-treatment week 48. An alternate endpoint would be ≥2 log reduction in HDV RNA combined with normalization of alanine aminotransferase level. Suitable candidates for phase II/III trials would be treatment-naiive or experienced patients with quantifiable HDV RNA. Novel biomarkers (hepatitis B core-related antigen [HBcrAg] and HBV RNA) remain exploratory, while nucleos(t)ide analogs and pegylated interferon still have a role in combination with novel agents. Importantly, patient input is encouraged early on in drug development under the FDA/EMA patient-focused drug development programs.
Copyright © 2023 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and European Association for the Study of the Liver. Published by Wolters Kluwer/Elsevier B.V. All Rights Reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest:
Marc G. Ghany: nothing to report.
Maria Buti: Advisory Board/Speaker Bureau for: Abbvie, Altimmune, Assembly, Antios, GlaxoSmithKline, Gilead Sciences, Janssen Roche Mercke Sharp and Dohme and Springbank
Pietro Lampertico: Advisory Board/Speaker Bureau for: Bristol Meyers Squibb, Roche, Gilead Sciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Abbvie, Mercke Sharp and Dohme, Arrowhead, Alnylam, Janssen, Springbank, MYR, Eiger, Antios, Aligos, VirBio.
Hannah Lee: nothing to report.
Figures
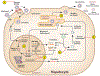

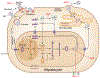

References
-
- Cornberg M, Lok AS, Terrault NA, Zoulim F, Faculty E-AHTEC. Guidance for design and endpoints of clinical trials in chronic hepatitis B - Report from the 2019 EASL-AASLD HBV Treatment Endpoints Conference(double dagger). J Hepatol 2020;72:539–557. - PubMed
-
- Yip TC, Wong GL, Chan HL, Tse YK, Lam KL, Lui GC, Wong VW. HBsAg seroclearance further reduces hepatocellular carcinoma risk after complete viral suppression with nucleos(t)ide analogues. J Hepatol 2019;70:361–370. - PubMed
-
- Yip TC, Wong VW, Lai MS, Lai JC, Hui VW, Liang LY, Tse YK, et al. Risk of hepatic decompensation but not hepatocellular carcinoma decreases over time in patients with hepatitis B surface antigen loss. J Hepatol 2022. - PubMed
-
- www.globalhep.org/sites/default/files/content/resource/files/2021-05/WHO.... Last accessed January 16th, 2023.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

