Allelic variation of KIR and HLA tunes the cytolytic payload and determines functional hierarchy of NK cell repertoires
- PMID: 37327114
- PMCID: PMC10440473
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023009827
Allelic variation of KIR and HLA tunes the cytolytic payload and determines functional hierarchy of NK cell repertoires
Abstract
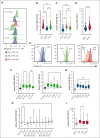
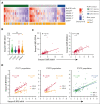
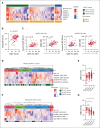
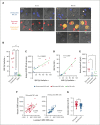
The functionality of natural killer (NK) cells is tuned during education and is associated with remodeling of the lysosomal compartment. We hypothesized that genetic variation in killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) and HLA, which is known to influence the functional strength of NK cells, fine-tunes the payload of effector molecules stored in secretory lysosomes. To address this possibility, we performed a high-resolution analysis of KIR and HLA class I genes in 365 blood donors and linked genotypes to granzyme B loading and functional phenotypes. We found that granzyme B levels varied across individuals but were stable over time in each individual and genetically determined by allelic variation in HLA class I genes. A broad mapping of surface receptors and lysosomal effector molecules revealed that DNAM-1 and granzyme B levels served as robust metric of the functional state in NK cells. Variation in granzyme B levels at rest was tightly linked to the lytic hit and downstream killing of major histocompatibility complex-deficient target cells. Together, these data provide insights into how variation in genetically hardwired receptor pairs tunes the releasable granzyme B pool in NK cells, resulting in predictable hierarchies in global NK cell function.
© 2023 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: K.-J.M. is a consultant with ownership interests at Fate Therapeutics and Vycellix; reports research funding from Fate Therapeutics, Oncopeptides, and Merck; has a royalty agreement with Fate Therapeutics through the licensing of intellectual property; and has received honoraria from Oncopeptides and Cytovia. B.Ö. is a consultant and has ownership interest at Vycellix, and receives research support from Affimed. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Lanier LL. NK cell recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:225–274. - PubMed
-
- Brodin P, Lakshmikanth T, Johansson S, Karre K, Hoglund P. The strength of inhibitory input during education quantitatively tunes the functional responsiveness of individual natural killer cells. Blood. 2009;113(11):2434–2441. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

