SAMHD1 impairs type I interferon induction through the MAVS, IKKε, and IRF7 signaling axis during viral infection
- PMID: 37328105
- PMCID: PMC10404699
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104925
SAMHD1 impairs type I interferon induction through the MAVS, IKKε, and IRF7 signaling axis during viral infection
Abstract
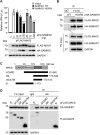
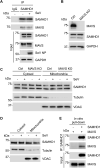
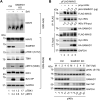
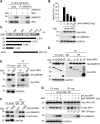
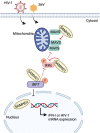
Sterile alpha motif and HD domain-containing protein 1 (SAMHD1) restricts human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection by reducing the intracellular dNTP pool. We have shown that SAMHD1 suppresses nuclear factor kappa-B activation and type I interferon (IFN-I) induction by viral infection and inflammatory stimuli. However, the mechanism by which SAMHD1 inhibits IFN-I remains unclear. Here, we show that SAMHD1 inhibits IFN-I activation induced by the mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein (MAVS). SAMHD1 interacted with MAVS and suppressed MAVS aggregation in response to Sendai virus infection in human monocytic THP-1 cells. This resulted in increased phosphorylation of TANK binding kinase 1 (TBK1), inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase epsilon (IKKε), and IFN regulatory factor 3 (IRF3). SAMHD1 suppressed IFN-I activation induced by IKKε and prevented IRF7 binding to the kinase domain of IKKε. We found that SAMHD1 interaction with the inhibitory domain (ID) of IRF7 (IRF7-ID) was necessary and sufficient for SAMHD1 suppression of IRF7-mediated IFN-I activation in HEK293T cells. Computational docking and molecular dynamics simulations revealed possible binding sites between IRF7-ID and full-length SAMHD1. Individual substitution of F411, E416, or V460 in IRF7-ID significantly reduced IRF7 transactivation activity and SAMHD1 binding. Furthermore, we investigated the role of SAMHD1 inhibition of IRF7-mediated IFN-I induction during HIV-1 infection. We found that THP-1 cells lacking IRF7 expression had reduced HIV-1 infection and viral transcription compared to control cells, indicating a positive role of IRF7 in HIV-1 infection. Our findings suggest that SAMHD1 suppresses IFN-I induction through the MAVS, IKKε, and IRF7 signaling axis.
Keywords: HIV-1; IKKε; IRF; MAVS; SAMHD1; innate immunity; interferon; molecular docking.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SAMHD1 suppresses innate immune responses to viral infections and inflammatory stimuli by inhibiting the NF-κB and interferon pathways.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Apr 17;115(16):E3798-E3807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1801213115. Epub 2018 Apr 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29610295 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccinia virus protein C6 is a virulence factor that binds TBK-1 adaptor proteins and inhibits activation of IRF3 and IRF7.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Sep;7(9):e1002247. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002247. Epub 2011 Sep 8. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 21931555 Free PMC article.
-
TRAF6 and TAK1 Contribute to SAMHD1-Mediated Negative Regulation of NF-κB Signaling.J Virol. 2021 Jan 13;95(3):e01970-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01970-20. Print 2021 Jan 13. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33177202 Free PMC article.
-
IRF7: role and regulation in immunity and autoimmunity.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 10;14:1236923. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1236923. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37638030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of differential expression of human interferon--a genes in antiviral immunity.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009 Aug;20(4):283-95. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2009.07.005. Epub 2009 Aug 3. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009. PMID: 19651532 Review.
Cited by
-
Aggravating mechanisms from COVID-19.Virol J. 2024 Sep 27;21(1):228. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02506-8. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 39334442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SAMHD1 deficiency enhances macrophage-mediated clearance of Salmonella Typhimurium via NF-κB activation in zebrafish.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 25;16:1509725. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1509725. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40352920 Free PMC article.
-
SAMHD1 enhances HIV-1-induced apoptosis in monocytic cells via the mitochondrial pathway.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 9:2025.01.08.632057. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.08.632057. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: mBio. 2025 Jul 9;16(7):e0042525. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00425-25. PMID: 39829911 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
dNTP depletion and beyond: the multifaceted nature of SAMHD1-mediated viral restriction.J Virol. 2025 May 20;99(5):e0030225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00302-25. Epub 2025 Apr 25. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40277359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SAMHD1 enhances HIV-1-induced apoptosis in monocytic cells via the mitochondrial pathway.mBio. 2025 Jul 9;16(7):e0042525. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00425-25. Epub 2025 May 28. mBio. 2025. PMID: 40434097 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goldstone D.C., Ennis-Adeniran V., Hedden J.J., Groom H.C., Rice G.I., Christodoulou E., et al. HIV-1 restriction factor SAMHD1 is a deoxynucleoside triphosphate triphosphohydrolase. Nature. 2011;480:379–382. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

