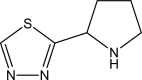
Multi-method evaluation of a 2-(1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-yl)pyrrolidine corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in HCl: combining gravimetric, electrochemical, and DFT approaches
- PMID: 37328536
- PMCID: PMC10276050
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-36252-8
Multi-method evaluation of a 2-(1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-yl)pyrrolidine corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in HCl: combining gravimetric, electrochemical, and DFT approaches
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Multi-method evaluation of a 2-(1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-yl)pyrrolidine corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in HCl: combining gravimetric, electrochemical, and DFT approaches.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 3;15(1):647. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-83688-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39753632 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
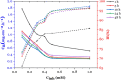
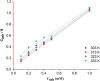
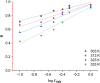
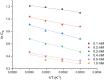
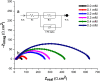
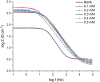
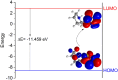
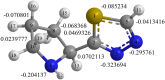
The corrosion inhibition properties of 2-(1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-yl)pyrrolidine (2-TP) on mild steel in a 1 M HCl solution were investigated using weight loss, potentiodynamic polarization, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and open circuit potential (OCP) measurements. In addition, DFT calculations were performed on 2-TP. The polarization curves revealed that 2-TP is a mixed-type inhibitor. The results indicate that 2-TP is an effective inhibitor for mild steel corrosion in a 1.0 M HCl solution, with an inhibition efficiency of 94.6% at 0.5 mM 2-TP. The study also examined the impact of temperature, revealing that the inhibition efficiency increases with an increasing concentration of 2-TP and decreases with a rise in temperature. The adsorption of the inhibitor on the mild steel surface followed the Langmuir adsorption isotherm, and the free energy value indicated that the adsorption of 2-TP is a spontaneous process that involves both physical and chemical adsorption mechanisms. The DFT calculations showed that the adsorption of 2-TP on the mild steel surface is mainly through the interaction of the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom of the thiadiazole ring with the metal surface. The results obtained from the weight loss, potentiodynamic polarization, EIS and OCP measurements were in good agreement with each other and confirmed the effectiveness of 2-TP as a corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in 1.0 M HCl solution. Overall, the study demonstrates the potential use of 2-TP as a corrosion inhibitor in acid environments.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Novel Corrosion Inhibitor for Mild Steel in HCl.Materials (Basel). 2014 Jan 27;7(2):662-672. doi: 10.3390/ma7020662. Materials (Basel). 2014. PMID: 28788482 Free PMC article.
-
Theoretical and Electrochemical Evaluation of Cannabis Sativa L. Extracts as Corrosion Inhibitors for Mild Steel in Acidic Medium.ChemistryOpen. 2025 May;14(5):e202400273. doi: 10.1002/open.202400273. Epub 2024 Dec 23. ChemistryOpen. 2025. PMID: 39715726 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effect of xanthan gum and synergistic surfactant additives for mild steel corrosion in 1M HCl.Carbohydr Polym. 2016 Jan 20;136:384-93. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.09.027. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Carbohydr Polym. 2016. PMID: 26572368
-
Corrosion Inhibition of Mild Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Environment Using Terephthaldehyde Based on Schiff Base: Gravimetric, Thermodynamic, and Computational Studies.Molecules. 2022 Jul 29;27(15):4857. doi: 10.3390/molecules27154857. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35956814 Free PMC article.
-
Innovation of Imine Metal Chelates as Corrosion Inhibitors at Different Media: A Collective Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 19;23(16):9360. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169360. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012623 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into the newly synthesized bi- Mannich base for carbon steel corrosion inhibition in H2S and HCl solution.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 27;14(1):19869. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70905-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39191811 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, docking and characterization of some novel 5-(S-alkyl)-1.3.4-thiadiazole-2-carboxamide derivatives as anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents.BMC Chem. 2024 Jul 27;18(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s13065-024-01237-9. BMC Chem. 2024. PMID: 39068479 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the corrosion inhibition behavior of prinivil drug on mild steel in 1M HCl corrosive solution: insights from density functional theory, molecular dynamics, and experimental approaches.Front Chem. 2024 Jun 13;12:1403118. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1403118. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 38947959 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive evaluation of 5-imino-1,2,4-dithiazolidine-3-thione as a corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 26;15(1):10349. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-95104-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40133609 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jain, A. K., Sharma, S., Vaidya, A., Ravichandran, V. & Agrawal, R. K. 1,3,4-thiadiazole and its derivatives: A review on recent progress in biological activities. Chem. Biol. Drug Des.81(5), 557–576. 10.1111/cbdd.12125 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Salim, R. D. et al. Corrosion inhibition of thiadiazole derivative for mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution. Int. J. Corros. Scale Inhib.9(2), 550–561. 10.17675/2305-6894-2020-9-2-10 (2020).
-
- Annon, I. A. et al. Corrosion inhibition of mild steel in hydrochloric acid environment using thiadiazole derivative: Weight loss, thermodynamics, adsorption and computational investigations. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng.41, 244–252. 10.1016/j.sajce.2022.06.011 (2022).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

