The impact of delayed gastric emptying as measured by gastric emptying scintigraphy on the outcome of magnetic sphincter augmentation
- PMID: 37328595
- PMCID: PMC10462528
- DOI: 10.1007/s00464-023-10190-y
The impact of delayed gastric emptying as measured by gastric emptying scintigraphy on the outcome of magnetic sphincter augmentation
Abstract
Introduction: The impact of delayed gastric emptying (DGE) on the outcome of anti-reflux surgery (ARS) is controversial. There is concern that poor gastric emptying diminishes outcomes. Magnetic sphincter augmentation (MSA) may have a comparatively mild impact on gastric physiology, but the relationship between DGE and MSA outcomes is unknown. This study aims to evaluate the relationship between objective DGE and MSA outcomes over time.
Methods: Patients who completed gastric emptying scintigraphy (GES) prior to MSA between 2013 and 2021 were included. DGE was defined as a 4 h retention > 10% or half emptying time > 90 min on GES. Outcomes were compared between DGE and normal gastric emptying (NGE) groups at 6 months, 1 and 2 years. Sub-analysis of patients with severe (> 35%) DGE and correlation analysis between 4-h retention and symptom and acid-normalization were performed.
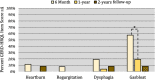
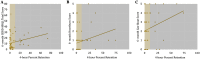
Results: The study population consisted of 26 (19.8%) patients with DGE and 105 with NGE. DGE was associated with more 90-days readmissions (18.5 vs 2.9%, p = 0.009). At 6 months patients with DGE had higher median (IQR) GERD-HRQL total [17.0(10-29) vs 5.5(3-16), p = 0.0013], heartburn [1(1-3) vs 0(0-1), p = 0.0010) and gas-bloat [4(2-5) vs 2(1-3), p = 0.033] scores. Outcomes at 1 and 2 years follow-up were comparable (p > 0.05). From 6 months to 1-year the gas-bloat score decreased from 4(2-5) to 3(1-3), p = 0.041. Total and heartburn scores decreased, but not significantly. Severe DGE (n = 4) patients had lower antiacid medication freedom at 6 months (75 vs 87%, p = 0.014) and 1-year (50 vs 92%, p = 0.046). There were non-significant trends for higher GERD-HRQL scores, dissatisfaction, and removal rates in severe DGE at 6 months and 1-year. There was a weak correlation between 4-h retention and 6-month GERD-HRQL total score [R = 0.253, 95%CI (0.09-0.41), p = 0.039], but not acid-normalization (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: Outcomes after MSA are diminished early on in patients with mild-to-moderate DGE, but comparable by 1 year and durable at 2 years. Severe DGE outcomes may be suboptimal.
Keywords: Bloating; Delated gastric emptying; Gastroparesis; Magnetic sphincter augmentation; Outcome.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Drs. Shahin Ayazi and Blair Jobe are on the scientific advisory board of Johnson and Johnson and receive consulting fee. Drs. Sven Eriksson, Ping Zheng, Inanc Sarici and Ms. Xinxin Shen have no conflicts of interest or financial disclosures.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Outcomes of Nissen fundoplication in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease and delayed gastric emptying.Arch Surg. 2009 Sep;144(9):823-8. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.2009.160. Arch Surg. 2009. PMID: 19797106
-
Gas-Bloat Syndrome after Magnetic Sphincter Augmentation: Incidence, Natural History, Risk Factors, and Impact on Surgical Outcomes Over Time.J Am Coll Surg. 2024 May 1;238(5):912-923. doi: 10.1097/XCS.0000000000000928. Epub 2023 Dec 20. J Am Coll Surg. 2024. PMID: 38116944 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed gastric emptying and typical scintigraphic gastric curves in children with gastroesophageal reflux disease: could pyloromyotomy improve this condition?J Pediatr Surg. 2011 May;46(5):863-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2011.02.015. J Pediatr Surg. 2011. PMID: 21616242
-
The International Study Group of Pancreatic Surgery definition of delayed gastric emptying and the effects of various surgical modifications on the occurrence of delayed gastric emptying after pancreatoduodenectomy.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2017 Aug 15;16(4):353-363. doi: 10.1016/S1499-3872(17)60037-7. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2017. PMID: 28823364 Review.
-
Gastric Emptying Scintigraphy Before Gastric per Oral Endoscopic Myotomy: Imaging May Inform Treatment.Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2019 Jan;29(1):127-137. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2018.08.014. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2019. PMID: 30396522 Review.
Cited by
-
Dumping Syndrome Post Hiatal Hernia Repair With the LINX Sphincter Augmentation Device.Cureus. 2025 Jun 12;17(6):e85893. doi: 10.7759/cureus.85893. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40656243 Free PMC article.
-
The failure pattern for the magnetic sphincter augmentation device: a single-institution case series with literature review.Surg Endosc. 2025 Aug;39(8):4956-4964. doi: 10.1007/s00464-025-11842-x. Epub 2025 Jun 26. Surg Endosc. 2025. PMID: 40571793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Food in Relation to Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD).Nutrients. 2023 Aug 15;15(16):3583. doi: 10.3390/nu15163583. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37630773 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

