One-week external beam partial breast irradiation: survival and toxicity outcomes
- PMID: 37329461
- PMCID: PMC11797670
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-023-04973-y
One-week external beam partial breast irradiation: survival and toxicity outcomes
Abstract
Purpose: According to ASTRO and ESTRO guidelines, external beam Partial Breast Irradiation (PBI) is a valid option for early-stage breast cancer patients. Nevertheless, there is lack of consensus about the best treatment schedule.
Methods: We retrospectively analysed data of female patients treated at our institution from 2013 to 2022 with adjuvant "one-week" partial breast irradiation. Clinical Target Volume (CTV) was an isotropic expansion of 15 mm from the tumour bed (identified as the breast tissue between surgical clips). The treatment schedule was 30 Gy delivered with Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy in 5 daily fractions. The primary endpoint was Local Control (LC). Disease-Free Survival (DFS), Overall Survival (OS) and safety were secondary endpoints.
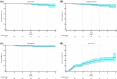
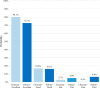
Results: Three hundred and forty-four patients with a median age of 69 (33-87) years were included in the study. After a median follow-up of 34 (7-105) months, 7 patients (2.0%) developed a local recurrence. Three-year LC, DFS and OS actuarial rates were 97.5% (95% CI 96.2%-98.8%), 95.7% (95% CI 94.2%-97.2%), and 96.9% (95% CI 95.7%-98.1%), respectively. Ten (2.9%) patients experienced grade 2 late toxicities. Five (1.5%) patients reported late cardiac major events. Three (0.9%) late pulmonary toxicities were detected. One hundred and five (30.5%) patients reported fat necrosis. Good or excellent cosmetic evaluation following the Harvard Scale was reported in 252 (96.9%) cases by the physicians, while in 241 (89.2%) cases by the patients.
Conclusion: "One-week" PBI is effective and safe, and this schedule is a valid option for highly selected early breast cancer patients.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Feasibility; Partial breast irradiation; Radiation therapy.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
This study was not funded. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study protocol was approved by the local ethical committee, with the registration number: INT 110/22. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants involved in the study.
Figures
References
-
- Bourgier C, Pichenot C, Verstraet R, El Nemr M, Heymann S, Biron B, Delaloge S, Mathieu MC, Garbay JR, Bourhis J, Taghian AG, Marsiglia H (2011) Early side effects of three-dimensional conformal external beam accelerated partial breast irradiation to a total dose of 40 Gy in one week (a phase II trial). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81(5):1228–1235. 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.07.040 - PubMed
-
- Ciabattoni A, Gregucci F, De Rose F et al (2022) AIRO breast cancer group best clinical practice 2022 update. Tumori J 108(2_suppl):1–144. 10.1177/03008916221088885 - PubMed
-
- Coles CE, Griffin CL, Kirby AM, Titley J, Agrawal RK, Alhasso A, Bhattacharya IS, Brunt AM et al (2017) Partial-breast radiotherapy after breast conservation surgery for patients with early breast cancer (UK IMPORT LOW trial): 5-year results from a multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 390(10099):1048–1060. 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31145-5 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical