GM1 oligosaccharide efficacy against α-synuclein aggregation and toxicity in vitro
- PMID: 37330108
- PMCID: PMC10579883
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2023.159350
GM1 oligosaccharide efficacy against α-synuclein aggregation and toxicity in vitro
Abstract
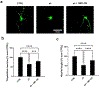
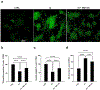
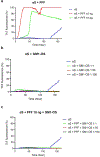
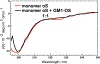
Fibrillary aggregated α-synuclein represents the neurologic hallmark of Parkinson's disease and is considered to play a causative role in the disease. Although the causes leading to α-synuclein aggregation are not clear, the GM1 ganglioside interaction is recognized to prevent this process. How GM1 exerts these functions is not completely clear, although a primary role of its soluble oligosaccharide (GM1-OS) is emerging. Indeed, we recently identified GM1-OS as the bioactive moiety responsible for GM1 neurotrophic and neuroprotective properties, specifically reverting the parkinsonian phenotype both in in vitro and in vivo models. Here, we report on GM1-OS efficacy against the α-synuclein aggregation and toxicity in vitro. By amyloid seeding aggregation assay and NMR spectroscopy, we demonstrated that GM1-OS was able to prevent both the spontaneous and the prion-like α-synuclein aggregation. Additionally, circular dichroism spectroscopy of recombinant monomeric α-synuclein showed that GM1-OS did not induce any change in α-synuclein secondary structure. Importantly, GM1-OS significantly increased neuronal survival and preserved neurite networks of dopaminergic neurons affected by α-synuclein oligomers, together with a reduction of microglia activation. These data further demonstrate that the ganglioside GM1 acts through its oligosaccharide also in preventing the α-synuclein pathogenic aggregation in Parkinson's disease, opening a perspective window for GM1-OS as drug candidate.
Keywords: GM1 ganglioside; GM1 oligosaccharide; Parkinson's disease; Plasma membrane signaling; α-Synuclein.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Chester MA: IUPAC-IUB Joint Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature (JCBN). Nomenclature of glycolipids--recommendations 1997. Eur J Biochem 257, 293–8 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Poewe W; Seppi K; Tanner CM; Halliday GM; Brundin P; Volkmann J; Schrag AE; Lang AE: Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers 3, 17013 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Ledeen RW; Wu G: Gangliosides, α-Synuclein, and Parkinson’s Disease. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 156, 435–454 (2018). - PubMed

