Exogenous DNA enhances DUOX2 expression and function in human pancreatic cancer cells by activating the cGAS-STING signaling pathway
- PMID: 37330147
- PMCID: PMC10527782
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.06.012
Exogenous DNA enhances DUOX2 expression and function in human pancreatic cancer cells by activating the cGAS-STING signaling pathway
Abstract
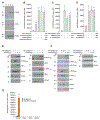
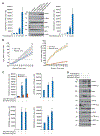
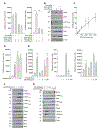
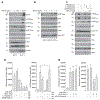
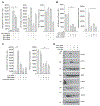
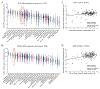
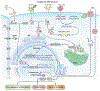
Pro-inflammatory cytokines upregulate the expression of the H2O2-producing NADPH oxidase dual oxidase 2 (DUOX2)2 which, when elevated, adversely affects survival from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Because the cGAS-STING pathway is known to initiate pro-inflammatory cytokine expression following uptake of exogenous DNA, we examined whether activation of cGAS-STING could play a role in the generation of reactive oxygen species by PDAC cells. Here, we found that a variety of exogenous DNA species markedly increased the production of cGAMP, the phosphorylation of TBK1 and IRF3, and the translocation of phosphorylated IRF3 into the nucleus, leading to a significant, IRF3-dependent enhancement of DUOX2 expression, and a significant flux of H2O2 in PDAC cells. However, unlike the canonical cGAS-STING pathway, DNA-related DUOX2 upregulation was not mediated by NF-κB. Although exogenous IFN-β significantly increased Stat1/2-associated DUOX2 expression, intracellular IFN-β signaling that followed cGAMP or DNA exposure did not itself increase DUOX2 levels. Finally, DUOX2 upregulation subsequent to cGAS-STING activation was accompanied by the enhanced, normoxic expression of HIF-1α and VEGF-A as well as DNA double strand cleavage, suggesting that cGAS-STING signaling may support the development of an oxidative, pro-angiogenic microenvironment that could contribute to the inflammation-related genetic instability of pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: Dual oxidase 2; Pancreatic cancer; Reactive oxygen species; STING; cGAS.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
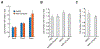
Similar articles
-
Dual oxidase 2 and pancreatic adenocarcinoma: IFN-γ-mediated dual oxidase 2 overexpression results in H2O2-induced, ERK-associated up-regulation of HIF-1α and VEGF-A.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 18;7(42):68412-68433. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12032. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27637085 Free PMC article.
-
IL-4 and IL-17A Cooperatively Promote Hydrogen Peroxide Production, Oxidative DNA Damage, and Upregulation of Dual Oxidase 2 in Human Colon and Pancreatic Cancer Cells.J Immunol. 2019 Nov 1;203(9):2532-2544. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800469. Epub 2019 Sep 23. J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31548328 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation and sustained activation of Stat1 are essential for interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma)-induced dual oxidase 2 (Duox2) and dual oxidase A2 (DuoxA2) expression in human pancreatic cancer cell lines.J Biol Chem. 2011 Apr 8;286(14):12245-56. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.191031. Epub 2011 Feb 14. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21321110 Free PMC article.
-
cGAS-STING Activation in the Tumor Microenvironment and Its Role in Cancer Immunity.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1024:175-194. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-5987-2_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28921470 Review.
-
cGAS-STING signaling pathway in intestinal homeostasis and diseases.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 14;14:1239142. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1239142. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37781354 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-605-3p may affect caerulein-induced ductal cell injury and pyroptosis in acute pancreatitis by targeting the DUOX2/NLRP3/NF-κB pathway.PeerJ. 2024 Aug 30;12:e17874. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17874. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39224819 Free PMC article.
-
cGAS/STING pathway and gastrointestinal cancer: Mechanisms and diagnostic and therapeutic targets (Review).Oncol Rep. 2025 Jan;53(1):15. doi: 10.3892/or.2024.8848. Epub 2024 Nov 29. Oncol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39611480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unlocking the therapeutic potential of the STING signaling pathway in anti-tumor treatment.Clin Exp Med. 2025 Aug 12;25(1):290. doi: 10.1007/s10238-025-01838-1. Clin Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 40794212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut epithelial Interleukin-17 receptor A signaling can modulate distant tumors growth through microbial regulation.Cancer Cell. 2024 Jan 8;42(1):85-100.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2023.12.006. Epub 2023 Dec 28. Cancer Cell. 2024. PMID: 38157865 Free PMC article.
-
IL-17A-producing NKp44(-) group 3 innate lymphoid cells accumulate in Familial Adenomatous Polyposis duodenal tissue.Nat Commun. 2025 Apr 25;16(1):3873. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-58907-y. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40280932 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aviello G, Knaus UG, NADPH oxidases and ROS signaling in the gastrointestinal tract. Mucosal Immunol 11 (2018) 1011–23. - PubMed
-
- De Deken X, Corvilain B, Dumont JE, Miot F, Roles of DUOX-mediated hydrogen peroxide in metabolism, host defense, and signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal 20 (2014) 2776–93. - PubMed
-
- Wu Y, Lu J, Antony S, Juhasz A, Liu H, Jiang G et al., Interferon-gamma-induced toll-like receptor 4 is required for the synergistic induction of dual oxidase 2 and dual oxidase A2 by lipopolysaccharide and interferon-gamma in human pancreatic cancer cell lines. J Immunol 190 (2013) 1859–72. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

