Epigenetic reprogramming of cell cycle genes by ACK1 promotes breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitor
- PMID: 37330596
- PMCID: PMC10348910
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-023-02747-x
Epigenetic reprogramming of cell cycle genes by ACK1 promotes breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitor
Abstract
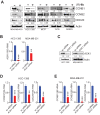
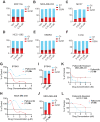
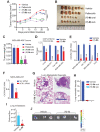
Hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancers exhibit high sensitivity to CDK4/6 inhibitors such as palbociclib. However, most patients inevitably develop resistance, thus identification of new actionable therapeutic targets to overcome the recurrent disease is an urgent need. Immunohistochemical studies of tissue microarray revealed increased activation of non-receptor tyrosine kinase, ACK1 (also known as TNK2) in most of the breast cancer subtypes, independent of their hormone receptor status. Chromatin immunoprecipitation studies demonstrated that the nuclear target of activated ACK1, pY88-H4 epigenetic marks, were deposited at cell cycle genes, CCNB1, CCNB2 and CDC20, which in turn initiated their efficient transcription. Pharmacological inhibition of ACK1 using its inhibitor, (R)-9b dampened CCNB1, CCNB2 and CDC20 expression, caused G2/M arrest, culminating in regression of palbociclib-resistant breast tumor growth. Further, (R)-9b suppressed expression of CXCR4 receptor, which resulted in significant impairment of metastasis of breast cancer cells to lung. Overall, our pre-clinical data identifies activated ACK1 as an oncogene that epigenetically controls the cell cycle genes governing the G2/M transition in breast cancer cells. ACK1 inhibitor, (R)-9b could be a novel therapeutic option for the breast cancer patients that have developed resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A patent “Inhibitors of ACK1/TNK2 Tyrosine Kinase” (patent no. 9,850,216; 10,017,478 and 10,336,734) covers (
Figures




References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Zhao W, Zhang Q, Kang X, Jin S, Lou C. AIB1 is required for the acquisition of epithelial growth factor receptor-mediated tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;380:699–704. - PubMed
-
- Nass N, Kalinski T. Tamoxifen resistance: from cell culture experiments towards novel biomarkers. Pathol Res Pr. 2015;211:189–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

