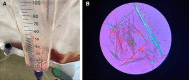
AKI in a Patient Treated for Herpes Simplex Virus Encephalitis
- PMID: 37332112
- PMCID: PMC10617796
- DOI: 10.34067/KID.0000000000000181
AKI in a Patient Treated for Herpes Simplex Virus Encephalitis
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Herpes Simplex Virus Encephalitis after Recovery from Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Rare Case Report.Intern Med. 2023 Dec 1;62(23):3515-3518. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1790-23. Epub 2023 Sep 29. Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 37779075 Free PMC article.
-
Varicella-zoster virus encephalitis resembling herpes simplex virus encephalitis.BMJ Case Rep. 2021 Dec 31;14(12):e247602. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2021-247602. BMJ Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34972787 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Fever with no elevation in inflammatory markers: herpes simplex virus encephalitis.QJM. 2021 Aug 29;114(5):326-327. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcab012. QJM. 2021. PMID: 33486506 No abstract available.
-
Herpes simplex virus infections of the central nervous system: encephalitis and meningitis, including Mollaret's.Herpes. 2004 Jun;11 Suppl 2:57A-64A. Herpes. 2004. PMID: 15319091 Review.
-
Herpes simplex virus-induced anti-N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor encephalitis: a systematic literature review with analysis of 43 cases.Dev Med Child Neurol. 2017 Aug;59(8):796-805. doi: 10.1111/dmcn.13448. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28439890
Cited by
-
The Role of Viral Infections in Acute Kidney Injury and Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Therapy.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2025 Jun;21(5):1199-1236. doi: 10.1007/s12015-025-10873-0. Epub 2025 Apr 8. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2025. PMID: 40198477 Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical