Holding the Belief That Gender Roles Can Change Reduces Women's Work-Family Conflict
- PMID: 37332232
- PMCID: PMC11504165
- DOI: 10.1177/01461672231178349
Holding the Belief That Gender Roles Can Change Reduces Women's Work-Family Conflict
Abstract
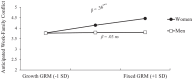
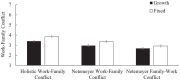
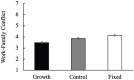
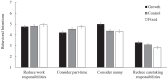
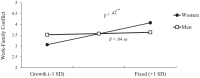
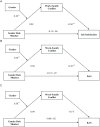
Across four studies (N = 1544), we examined the relationship between individuals' gender role mindsets, or beliefs about the malleability versus fixedness of traditional gender roles, and work-family conflict. We found that undergraduate women (but not men) business students holding a fixed, compared to growth, gender role mindset anticipated more work-family conflict. Next, we manipulated gender role mindset and demonstrated a causal link between women's growth mindsets (relative to fixed mindsets and control conditions) and reduced work-family conflict. We showed mechanistically that growth gender role mindsets unburden women from prescriptive gender roles, reducing work-family conflict. Finally, during COVID-19, we demonstrated a similar pattern among working women in high-achieving dual-career couples. We found an indirect effect of women's gender role mindset on job and relationship satisfaction, mediated through work-family conflict. Our preregistered studies suggest that holding the belief that gender roles can change mitigates women's work-family conflict.
Keywords: COVID-19; gender differences; gender roles; mindsets; work–family conflict.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Abdullah N.-A., Adenan N. F. b., Zaiedy N. S. I. M. (2021). Relationship between work-family conflict, organizational commitment and welfare in the workplace among working women. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 11(3), 154–168.
-
- Ain Tommar S., Kolokolova O., Mura R. (2022). When paid work gives in to unpaid care work: Evidence from the hedge fund industry under COVID-19. Management Science, 68, 5557–6354. 10.1287/mnsc.2022.4402 - DOI
-
- Balzer W. K., Kihm J. A., Smith P. C., Irwin J. L., Bachiochi P. D., Robie C., Sinar, E. F., & Parra, L. F. (1997). Users’ manual for the Job Descriptive Index (JDI; 1997 revision) and the job in general scales. Bowling Green, OH: Bowling Green State University.
-
- Bao H. W. S. (2021). bruceR: Broadly useful convenient and efficient R functions (R Package Version 0.8.10). https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=bruceR
-
- Bartoń K. (2022). MuMIn: Multi-model inference (R Package Version 1.46.0). https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=MuMIn
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

