Recent advances of exosomes in age-related macular degeneration
- PMID: 37332352
- PMCID: PMC10272348
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1204351
Recent advances of exosomes in age-related macular degeneration
Abstract
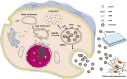
Exosomes are 30-150 nm extracellular vesicles that are secreted by almost all types of cells. Exosomes contain a variety of biologically active substances, such as proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids, and are important in the intercellular communication of biological mediators involved in nerve injury and repair, vascular regeneration, immune response, fibrosis formation, and many other pathophysiological processes. Although it has been extensively studied in the field of cancer, the exploration of ocular diseases has only just begun. Here, we discuss the latest developments in exosomes for age-related macular degeneration (AMD), including the pathogenesis of exosomes in age-related macular degeneration, their potential as diagnostic markers, and therapeutic vectors of the disease. Finally, the study of exosomes in age-related macular degeneration is still relatively few, and more detailed basic research and clinical trials are needed to verify its application in treatment and diagnosis, so as to adopt more personalized diagnosis and treatment strategies to stop the progression of age-related macular degeneration.
Keywords: age-related macular degeneration; diagnosis; exosomes; pathogenesis; treatment.
Copyright © 2023 Gu, Jiang and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Atienzar-Aroca S., Flores-Bellver M., Serrano-Heras G., Martinez-Gil N., Barcia J. M., Aparicio S., et al. (2016). Oxidative stress in retinal pigment epithelium cells increases exosome secretion and promotes angiogenesis in endothelial cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 20 (8), 1457–1466. 10.1111/jcmm.12834 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

