Volumetric fluid analysis of fixed monthly anti-VEGF treatment in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration
- PMID: 37332546
- PMCID: PMC10250951
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2023.06.12
Volumetric fluid analysis of fixed monthly anti-VEGF treatment in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate visual outcomes and changes in fluid after administering monthly anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) injections to treat neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD) with subretinal fluid (SRF) and pigment epithelial detachment (PED).
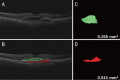
Methods: This prospective study included eyes with nAMD previously treated with as-needed anti-VEGF injections. The patients were treated with six monthly intravitreal injections of ranibizumab. Quantitative volumetric segmentation analyses of the SRF and PED were performed. The main outcome measures included best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), and SRF and PED volumes.
Results: Twenty eyes of 20 patients were included in this study. At the 6-month follow-up, BCVA and PED volume did not change significantly (P=0.110 and 0.999, respectively) but the mean SRF volume decreased from 0.53±0.82 mm3 at baseline to 0.08±0.23 mm3 (P=0.002). The absorption rate of the SRF volume was negatively correlated with the duration of previous anti-VEGF treatment (P=0.029). Seven of the 20 eyes (35%) showed a fluid-free macula and significant improvement in BCVA (P=0.036) by month 6.
Conclusion: Quantifying the SRF can precisely determine the patient's responsiveness to anti-VEGF treatment of nAMD.
Keywords: anti-vascular endothelial growth factor treatment; drug tolerance; neovascular age-related macular degeneration; persistent subretinal fluid; volumetric fluid analysis.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Figures


References
-
- Brown DM, Chen E, Mariani A, Major JC, Jr, Study Group Jr S Super-dose anti-VEGF (SAVE) trial: 2.0 mg intravitreal ranibizumab for recalcitrant neovascular macular degeneration-primary end point. Ophthalmology. 2013;120(2):349–354. - PubMed
-
- Stewart MW, Rosenfeld PJ, Penha FM, Wang FH, Yehoshua Z, Bueno-Lopez E, Lopez PF. Pharmacokinetic rationale for dosing every 2 weeks versus 4 weeks with intravitreal ranibizumab, bevacizumab, and aflibercept (vascular endothelial growth factor Trap-eye) Retina. 2012;32(3):434–457. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
