All-trans retinoic acid regulates the expression of MMP-2 and TGF-β2 via RDH5 in retinal pigment epithelium cells
- PMID: 37332553
- PMCID: PMC10250953
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2023.06.03
All-trans retinoic acid regulates the expression of MMP-2 and TGF-β2 via RDH5 in retinal pigment epithelium cells
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effect of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) on retinol dehydrogenase 5 (RDH5), matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and transforming growth factor-β2 (TGF-β2) transcription levels, and the effect of RDH5 on MMP-2 and TGF-β2 in retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells.
Methods: After adult RPE cell line-19 (ARPE-19 cells) intervened with gradient concentrations of ATRA (0-20 µmol/L) for 24h, flow cytometry was used to detect the proliferation and apoptosis of cells in each group, and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was used to detect RDH5, MMP-2 and TGF-β2 mRNA expression. Then, after ARPE-19 cells transfected with three different siRNA targets for 48h, the RDH5 knockdown efficiency of each group and expression of MMP-2 and TGF-β2 mRNA within them was detected by qRT-PCR.
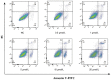
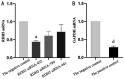
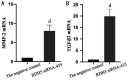
Results: Flow cytometry results showed that ATRA could inhibit the proliferation of RPE cells and promote the apoptosis of RPE cells, and the difference of apoptosis was statistically significant when the ATRA concentration exceeded 5 µmol/L and compared with the normal control group (P=0.027 and P=0.031, respectively). qRT-PCR results showed that ATRA could significantly inhibit the expression level of RDH5 mRNA (P<0.001) and promote the expression of MMP-2 and TGF-β2 mRNA (P=0.03 and P<0.001, respectively) in a dose-dependent manner, especially when treated with 5 µmol/L ATRA. The knockdown efficiency of RDH5 siRNA varies with different targets, among which RDH5 siRNA-435 had the highest knockdown efficiency, i.e., more than 50% lower than that of the negative control group (P=0.02). When RDH5 was knocked down for 48h, the results of qRT-PCR showed that the expressions of MMP-2 and TGF-β2 mRNA were significantly up-regulated (P<0.001).
Conclusion: ATRA inhibits the expression of RDH5 and promotes MMP-2 and TGF-β2, and further RDH5 knockdown significantly upregulates MMP-2 and TGF-β2. These findings suggest that RDH5 may be involved in an epithelial-mesenchymal transition of RPE cells mediated by ATRA.
Keywords: ARPE-19; all-trans retinoic acid; matrix metalloproteinase-2; retinol dehydrogenase 5; transforming growth factor-β2.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Figures
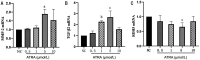
Similar articles
-
The Expression of Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 and Matrix Metalloproteinase 2 through Retinoic Acid Receptor Beta Induced by All-Trans Retinoic Acid in Cultured ARPE-19 Cells.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 11;11(3):e0150831. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150831. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26967733 Free PMC article.
-
All-trans retinoic acid stimulates the secretion of TGF-β2 via the phospholipase C but not the adenylyl cyclase signaling pathway in retinal pigment epithelium cells.BMC Ophthalmol. 2019 Jan 18;19(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12886-018-1017-6. BMC Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 30658598 Free PMC article.
-
Eupatilin attenuates TGF-β2-induced proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of retinal pigment epithelial cells.Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2021 Jun;40(2):103-114. doi: 10.1080/15569527.2021.1902343. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33719768
-
TGF-β2 promotes RPE cell invasion into a collagen gel by mediating urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) expression.Exp Eye Res. 2013 Oct;115:13-21. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2013.06.020. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Exp Eye Res. 2013. PMID: 23810810
-
Blockade of Jagged/Notch pathway abrogates transforming growth factor β2-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human retinal pigment epithelium cells.Curr Mol Med. 2014 May;14(4):523-34. doi: 10.2174/1566524014666140331230411. Curr Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24694299 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic signatures of retinal pigment epithelium-derived exosomes in myopic and non-myopic tree shrew eyes.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 22;12:1523211. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1523211. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40330779 Free PMC article.
-
Unexpected and Synergistical Effects of All-Trans Retinoic Acid and TGF-β2 on Biological Aspects of 2D and 3D Cultured ARPE19 Cells.Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 30;12(10):2228. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102228. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457541 Free PMC article.
-
RDH12-associated retinal degeneration caused by a homozygous pathogenic variant of 146C>T and literature review.Int J Ophthalmol. 2024 Feb 18;17(2):311-316. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2024.02.13. eCollection 2024. Int J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38371258 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omic analyses identify molecular targets of Chd7 that mediate CHARGE syndrome model phenotypes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 29:2025.07.28.666396. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.28.666396. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40766592 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Cone-rod homeobox transcriptionally activates TCF7 to promote the proliferation of retinal pigment epithelial and retinoblastoma cells in vitro.Int J Ophthalmol. 2024 Nov 18;17(11):1995-2006. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2024.11.04. eCollection 2024. Int J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39559312 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yan TY, Yang N, Hu W, Zhang XX, Li XD, Wang YJ, Kong J. Differentiation and maturation effect of all-trans retinoic acid on cultured fetal RPE and stem cell-derived RPE cells for cell-based therapy. Curr Eye Res. 2022;47(9):1300–1311. - PubMed
-
- Mao JF, Liu SZ. Regulation of RPE barrier function by all-trans retinoic acid in myopia. Neurosci Lett. 2014;568:17–22. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
