Hypoxia-inducible factor activation promotes osteogenic transition of valve interstitial cells and accelerates aortic valve calcification in a mice model of chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 37332579
- PMCID: PMC10272757
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1168339
Hypoxia-inducible factor activation promotes osteogenic transition of valve interstitial cells and accelerates aortic valve calcification in a mice model of chronic kidney disease
Abstract
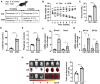
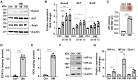
Introduction: Valve calcification (VC) is a widespread complication in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients. VC is an active process with the involvement of in situ osteogenic transition of valve interstitial cells (VICs). VC is accompanied by the activation of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) pathway, but the role of HIF activation in the calcification process remains undiscovered.
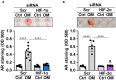
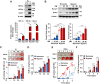
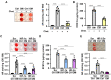
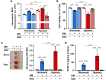
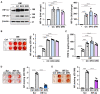
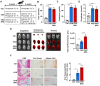
Methods and result: Using in vitro and in vivo approaches we addressed the role of HIF activation in osteogenic transition of VICs and CKD-associated VC. Elevation of osteogenic (Runx2, Sox9) and HIF activation markers (HIF-1α and HIF-2α) and VC occurred in adenine-induced CKD mice. High phosphate (Pi) induced upregulation of osteogenic (Runx2, alkaline-phosphatase, Sox9, osteocalcin) and hypoxia markers (HIF-1α, HIF-2α, Glut-1), and calcification in VICs. Down-regulation of HIF-1α and HIF-2α inhibited, whereas further activation of HIF pathway by hypoxic exposure (1% O2) or hypoxia mimetics [desferrioxamine, CoCl2, Daprodustat (DPD)] promoted Pi-induced calcification of VICs. Pi augmented the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and decreased viability of VICs, whose effects were further exacerbated by hypoxia. N-acetyl cysteine inhibited Pi-induced ROS production, cell death and calcification under both normoxic and hypoxic conditions. DPD treatment corrected anemia but promoted aortic VC in the CKD mice model.
Discussion: HIF activation plays a fundamental role in Pi-induced osteogenic transition of VICs and CKD-induced VC. The cellular mechanism involves stabilization of HIF-1α and HIF-2α, increased ROS production and cell death. Targeting the HIF pathways may thus be investigated as a therapeutic approach to attenuate aortic VC.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; hypoxia; hypoxia inducible factor; osteogenic differentiation; reactive oxygen species; valve calcification; valve interstitial cell.
© 2023 Csiki, Ababneh, Tóth, Lente, Szöőr, Tóth, Fillér, Juhász, Nagy, Balogh and Jeney.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

