The role of monocytes in thrombotic diseases: a review
- PMID: 37332592
- PMCID: PMC10272466
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1113827
The role of monocytes in thrombotic diseases: a review
Abstract
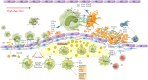
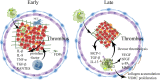
Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases are the number one killer threatening people's life and health, among which cardiovascular thrombotic events are the most common. As the cause of particularly serious cardiovascular events, thrombosis can trigger fatal crises such as acute coronary syndrome (myocardial infarction and unstable angina), cerebral infarction and so on. Circulating monocytes are an important part of innate immunity. Their main physiological functions are phagocytosis, removal of injured and senescent cells and their debris, and development into macrophages and dendritic cells. At the same time, they also participate in the pathophysiological processes of pro-coagulation and anticoagulation. According to recent studies, monocytes have been found to play a significant role in thrombosis and thrombotic diseases of the immune system. In this manuscript, we review the relationship between monocyte subsets and cardiovascular thrombotic events and analyze the role of monocytes in arterial thrombosis and their involvement in intravenous thrombolysis. Finally, we summarize the mechanism and therapeutic regimen of monocyte and thrombosis in hypertension, antiphospholipid syndrome, atherosclerosis, rheumatic heart disease, lower extremity deep venous thrombosis, and diabetic nephropathy.
Keywords: arterial thrombosis; intravenous thrombolysis; macrophage; monocyte; thrombotic diseases.
© 2023 Han, Liu, Li, Zhang, You, Lin, Wang, Gou, Wang, Zhou, Cai, Yuan and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The role of monocytes in thrombotic disorders. Insights from tissue factor, monocyte-platelet aggregates and novel mechanisms.Thromb Haemost. 2009 Nov;102(5):916-24. doi: 10.1160/TH09-01-0023. Thromb Haemost. 2009. PMID: 19888530 Review.
-
Smoking and use of oral contraceptives: impact on thrombotic diseases.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999 Jun;180(6 Pt 2):S357-63. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(99)70696-4. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999. PMID: 10368521
-
Cardiovascular Disease in Antiphospholipid Syndrome.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2020;18(6):538-548. doi: 10.2174/1570161117666190830101341. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31530257 Review.
-
Antiphospholipid syndrome and the risk of myocardial infarction: current evidence and uncertainties.Kardiol Pol. 2020 Jan 24;78(1):6-14. doi: 10.33963/KP.15090. Epub 2019 Dec 6. Kardiol Pol. 2020. PMID: 31808421 Review.
-
Cerebrovascular complications in cancer patients.Neurol Clin. 2003 Feb;21(1):167-92. doi: 10.1016/s0733-8619(02)00066-x. Neurol Clin. 2003. PMID: 12690649 Review.
Cited by
-
Can complement activation be the missing link in antiphospholipid syndrome?Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024 Dec 1;63(12):3243-3254. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keae178. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024. PMID: 38483257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of inflammatory microenvironment formation in cardiometabolic diseases: molecular and cellular perspectives.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jan 14;11:1529903. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1529903. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 39877020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flow Cytometry Evaluation of Blood-Cell-Bound Surface FVIII in Hemophilia A and Thrombosis.Cells. 2025 Jan 8;14(2):73. doi: 10.3390/cells14020073. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39851501 Free PMC article.
-
Monocyte/macrophage-mediated venous thrombus resolution.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 19;15:1429523. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1429523. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39100675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Causal relationship between immune cells and venous thromboembolism: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Thromb J. 2025 Aug 5;23(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s12959-025-00754-4. Thromb J. 2025. PMID: 40764987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- GBD 2017 SDG Collaborators: Lozano R, Fullman N, Abate D, Abay SM, Abbafati C, Abbasi N, et al. Measuring progress from 19 90 to 2017 and projecting attainment to 2030 of the health-related sustainable development goals for 195 countries and territories: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet. (2018) 392(10159):2091–138. 10.1016/s0140-6736(18)32281-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

