The Impacts of Family Educational Investment on Mental Health of Chinese Parents: Mediating and Moderating Effects
- PMID: 37332771
- PMCID: PMC10272405
- DOI: 10.3389/ijph.2023.1605566
The Impacts of Family Educational Investment on Mental Health of Chinese Parents: Mediating and Moderating Effects
Abstract
Objectives: This review aims to explore the impact of family educational investment on parents' mental health in China. Through this study, we reveal the current public health challenges and propose some solutions. Methods: Family educational investment takes three forms: economic investment, emotional investment, and time investment. This study examined the mediating effect of social integration and the moderating effect of social participation and workload on the relationship between family educational investment and parental mental health. Results: Economic investment, emotional investment and time investment were all negatively correlated with parental mental health. Social integration could better explain the detrimental effects of family educational investment on parental mental health, and that social participation and workload could play a significant negative and positive moderating role, respectively. Conclusion: Family educational investment, particularly emotional investment, plays an important and negative role in influencing parental mental health. To cope with the increased pressure brought about by educational competition, the state, society, and individuals all need to take measures.
Keywords: family educational investment; measures; parental mental health; social integration; social participation; workload.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have any conflicts of interest.
Figures

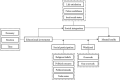



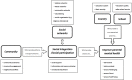
References
-
- James E. College Quality and Future Earnings: where Should You Send Your Child to College? Am Econ Rev (1989) 79(2):247–52.
-
- Useem M, Jerome K. Pathways to Top Corporate Management. Am Sociological Rev (1986) 51:184–200. 10.2307/2095515 - DOI
-
- Lu J, Pan T, Pan J, Zhou M, Zhang M, Hu S. Shadow Education in China and its Diversified Normative Governance Mechanism: Double Reduction Policy and Internet Public Opinion. Sustainability (2023) 15(2):1437. 10.3390/su15021437 - DOI
-
- Kaplan BH. Social Support and Health. Med Care (1977) 15(5):47–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

