Unroasted Green Coffee Extract-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Enhancing Intestinal Permeation
- PMID: 37332788
- PMCID: PMC10268626
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c06629
Unroasted Green Coffee Extract-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Enhancing Intestinal Permeation
Abstract
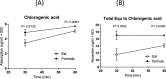
Green coffee bean extract (GCBE) provides diversified health benefits. However, its reported low bioavailability impeded its utilization in various applications. In this study, GCBE-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) were prepared to improve the bioavailability through enhanced intestinal absorption of GCBE. During the preparation of promising GCBE-loaded SLNs, the lipid concentration, surfactant concentration, and co-surfactant amount are crucial that were optimized using the Box-Behnken design, while particle size, polydispersity index (PDI), ζ-potential, entrapment efficiency, and cumulative drug release were the measured responses. GCBE-SLNs were successfully developed by a high shear homogenization technique using geleol as a solid lipid, tween 80 as a surfactant, and propylene glycol as Co-SAA. The optimized SLNs contained 5.8% geleol, 5.9% tween 80, and 80.4 mg PG resulting in a small particle size of 235.7 ± 12.5 nm, reasonably acceptable PDI of 0.417 ± 0.023, and ζ-potential of -15 ± 0.14 mV, with a high entrapment efficiency of 58.3 ± 0.85% and cumulative release of 7575 ± 0.78%. Furthermore, the performance of the optimized GCBE-SLN was evaluated using an ex vivo everted sac model where the intestinal permeation of GCBE was improved due to nanoencapsulation using SLN. Consequently, the results enlightened the auspicious potential of exploiting oral GCBE-SLNs for boosting intestinal absorption of chlorogenic acid.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Formulation, Characterization, and Evaluation of Eudragit-Coated Saxagliptin Nanoparticles Using 3 Factorial Design Modules.Molecules. 2022 Nov 3;27(21):7510. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217510. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364338 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation, Statistical Optimization and Characterization of Propolis-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Using Box-Behnken Design.Adv Pharm Bull. 2021 Feb;11(2):301-310. doi: 10.34172/apb.2021.043. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Adv Pharm Bull. 2021. PMID: 33880352 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation development of linagliptin solid lipid nanoparticles for oral bioavailability enhancement: role of P-gp inhibition.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2021 Jun;11(3):1166-1185. doi: 10.1007/s13346-020-00839-9. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 32804301
-
Formulation Design, Optimization, and Evaluation of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Loaded With an Antiviral Drug Tenofovir Using Box-Behnken Design for Boosting Oral Bioavailability.Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2024 Dec 31;2024:5248746. doi: 10.1155/2024/5248746. eCollection 2024. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 39781028 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of methazolamide-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for ophthalmic delivery using Box-Behnken design.J Liposome Res. 2014 Sep;24(3):171-81. doi: 10.3109/08982104.2014.891231. Epub 2014 Mar 10. J Liposome Res. 2014. PMID: 24611687 Review.
References
-
- Masek A.; Latos-Brozio M.; Kałuzna-Czaplińska J.; Rosiak A.; Chrzescijanska E. Antioxidant Properties of Green Coffee Extract. Forests 2020, 11, 557.10.3390/F11050557. - DOI
-
- Amigo-Benavent M.; Wang S.; Mateos R.; Sarriá B.; Bravo L. Antiproliferative and Cytotoxic Effects of Green Coffee and Yerba Mate Extracts, Their Main Hydroxycinnamic Acids, Methylxanthine and Metabolites in Different Human Cell Lines. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 106, 125–138. 10.1016/j.fct.2017.05.019. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Khojah E. Y. Effect of Arabic and Green Coffee Beans on Lowering Lipid Profile Parameters in Male Rats. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2016, 10, 310–317.
-
- Asbaghi O.; Sadeghian M.; Nasiri M.; Khodadost M.; Shokri A.; Panahande B.; Pirouzi A.; Sadeghi O. The Effects of Green Coffee Extract Supplementation on Glycemic Indices and Lipid Profile in Adults: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. Nutr. J. 2020, 19, 71.10.1186/s12937-020-00587-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

