Simultaneous bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbons and production of biofuels by the micro-green alga, cyanobacteria, and its consortium
- PMID: 37332941
- PMCID: PMC10272320
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16656
Simultaneous bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbons and production of biofuels by the micro-green alga, cyanobacteria, and its consortium
Abstract
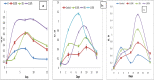
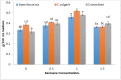
There are two major problems in the world, fuel deficiency and environmental pollution by fossil fuels. Microalgae are regarded as one of the most feasible feedstocks for the manufacturing of biofuels and are used in the degradation of fossil fuel spills. The present study was possessed to investigate the ability of green alga Chlorella vulgaris, blue-green alga Synechococcus sp, and its consortium to grow and degrade hydrocarbon such as kerosene (k) with different concentrations (0, 0.5, 1, and 1,5%), and also using algal biomasses to produce biofuel. The algal growth was estimated by optical density (O.D) at 600 nm, pigment contents such as Chlorophyll a,b carotenoid, and dry weight. The kerosene degradation was estimated by FT-IR analysis after and before the cultivation of algae and its consortium. The components of the methanol extract were determined by GC-MS spectroscopy. The results denote the best growth was determined by O.D, algae consortium with 1.5% Kerosene after ten days, meanwhile, the highest dry weight was with C. vulgaris after ten days of cultivation. The FT-IR demonstrated the algae and consortium possessed high efficacy to degrade kerosene. After 15 days of algae cultivation with 1% K, C.vulgaris produced the maximum amount of lipids (32%). The GC-MS profile of methanol extract of two algae and consortium demonstrated that Undecane was presented in high amounts, C.vulgaris (19.9%), Synechococcussp (82.16%), algae consortium (79.51%), and also were presented moderate amounts of fatty acid methyl ester in Synechococcus sp. Overall, our results indicate that a consortium of algae can absorb and remove kerosene from water, and at the same time produce biofuels like biodiesel and petroleum-based fuels.
Keywords: Algae consortium; Biodegradation; Kerosene; Lipids; Mixotrophic; Pollution.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Ite A.E., Harry T.A., Obadimu C.O., Asuaiko E.R., Inim I.J. Petroleum hydrocarbons contamination of surface water and groundwater in the Niger Delta region of Nigeria. J. Environ. Pollut. Hum. Health. 2018;6(2):51–61.
-
- Mohanakrishna G., Al-Raoush R.I., Abu-Reesh I.M., Aljaml K. Removal of petroleum hydrocarbons and sulfates from produced water using different bioelectrochemical reactor configurations. Sci. Total Environ. 2019;665:820–827. - PubMed
-
- Kondaveeti S., Govindarajan D., Mohanakrishna G., Thatikayala D., Abu-Reesh I.M., Min B.…Aminabhavi T.M. Sustainable bioelectrochemical systems for bioenergy generation via waste treatment from petroleum industries. Fuel. 2023;331
-
- Bu H., Tan X., Li S., Zhang Q. Water quality assessment of the Jinshui River(China) using multivariate statistical techniques. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010;60:1631–1639.
-
- Mnif I., Ellouze-Chaabouni S., Ayedi Y., Ghribi D. Treatment of diesel‐and kerosene‐contaminated water by B. subtilis SPB1 biosurfactant‐producing strain. Water Environ. Res. 2014;86(8):707–716. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

