This is a preprint.
Calretinin-expressing islet cells: a source of pre- and post-synaptic inhibition of non-peptidergic nociceptor input to the mouse spinal cord
- PMID: 37333120
- PMCID: PMC10274676
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.06.01.543241
Calretinin-expressing islet cells: a source of pre- and post-synaptic inhibition of non-peptidergic nociceptor input to the mouse spinal cord
Update in
-
Calretinin-expressing islet cells are a source of pre- and post-synaptic inhibition of non-peptidergic nociceptor input to the mouse spinal cord.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 18;13(1):11561. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-38605-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37464016 Free PMC article.
Abstract
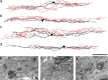
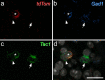
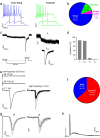
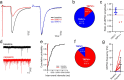
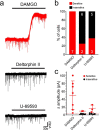
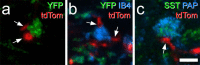
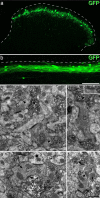
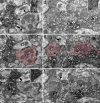
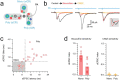
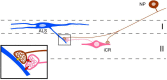
Unmyelinated non-peptidergic nociceptors (NP afferents) arborise in lamina II of the spinal cord and receive GABAergic axoaxonic synapses, which mediate presynaptic inhibition. However, until now the source of this axoaxonic synaptic input was not known. Here we provide evidence that it originates from a population of inhibitory calretinin-expressing interneurons (iCRs), which correspond to lamina II islet cells. The NP afferents can be assigned to 3 functionally distinct classes (NP1-3). NP1 afferents have been implicated in pathological pain states, while NP2 and NP3 afferents also function as pruritoceptors. Our findings suggest that all 3 of these afferent types innervate iCRs and receive axoaxonic synapses from them, providing feedback inhibition of NP input. The iCRs also form axodendritic synapses, and their targets include cells that are themselves innervated by the NP afferents, thus allowing for feedforward inhibition. The iCRs are therefore ideally placed to control the input from non-peptidergic nociceptors and pruritoceptors to other dorsal horn neurons, and thus represent a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of chronic pain and itch.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTEREST
The authors declare no competing financial or non-financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Snider W. D. & McMahon S. B. Tackling pain at the source: new ideas about nociceptors. Neuron 20, 629–632 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Ribeiro-da-Silva A. Ultrastructural features of the colocalization of calcitonin gene related peptide with substance P or somatostatin in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 73, 940–944 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Ribeiro-da-Silva A. & Coimbra A. Two types of synaptic glomeruli and their distribution in laminae I-III of the rat spinal cord. J Comp Neurol 209, 176–186 (1982). - PubMed
-
- Gerke M. B. & Plenderleith M. B. Ultrastructural analysis of the central terminals of primary sensory neurones labelled by transganglionic transport of bandeiraea simplicifolia I-isolectin B4. Neuroscience 127, 165–175 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
