This is a preprint.
Boundary Bypass Activity in the Abdominal-B Region of the Drosophila Bithorax Complex is Position Dependent and Regulated
- PMID: 37333165
- PMCID: PMC10274778
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.06.06.543971
Boundary Bypass Activity in the Abdominal-B Region of the Drosophila Bithorax Complex is Position Dependent and Regulated
Update in
-
Boundary bypass activity in the abdominal-B region of the Drosophila bithorax complex is position dependent and regulated.Open Biol. 2023 Aug;13(8):230035. doi: 10.1098/rsob.230035. Epub 2023 Aug 16. Open Biol. 2023. PMID: 37582404 Free PMC article.
Abstract
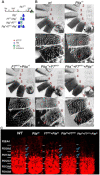
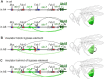
Expression of Abdominal-B ( Abd-B ) in abdominal segments A5 - A8 is controlled by four regulatory domains, iab-5 - iab-8 . Each domain has an initiator element (which sets the activity state), elements that maintain this state and tissue-specific enhancers. To ensure their functional autonomy, each domain is bracketed by boundary elements ( Mcp , Fab-7 , Fab-7 and Fab-8 ). In addition to blocking crosstalk between adjacent regulatory domains, the Fab boundaries must also have bypass activity so the relevant regulatory domains can "jump over" intervening boundaries and activate the Abd-B promoter. In the studies reported here we have investigated the parameters governing bypass activity. We find that the bypass elements in the Fab-7 and Fab-8 boundaries must be located in the regulatory domain that is responsible for driving Abd-B expression. We suggest that bypass activity may also be subject to regulation.
Summary statement: Boundaries separating Abd-B regulatory domains block crosstalk between domains and mediate their interactions with Abd-B . The latter function is location but not orientation dependent.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
