This is a preprint.
Multi-dose enteral L-citrulline administration in premature infants at risk of developing pulmonary hypertension associated with bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- PMID: 37333204
- PMCID: PMC10275028
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3006963/v1
Multi-dose enteral L-citrulline administration in premature infants at risk of developing pulmonary hypertension associated with bronchopulmonary dysplasia
Update in
-
Multi-dose enteral L-citrulline administration in premature infants at risk of developing pulmonary hypertension associated with bronchopulmonary dysplasia.J Perinatol. 2024 Feb;44(2):280-287. doi: 10.1038/s41372-023-01809-y. Epub 2023 Oct 31. J Perinatol. 2024. PMID: 37907796 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Abstract
Objective: Information is needed to guide the design of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating L-citrulline as a therapy for premature infants with pulmonary hypertension associated with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD-PH). Our goal was to evaluate the tolerability and ability to achieve a target steady-state L-citrulline plasma concentration in prematures treated enterally with a multi-dose L-citrulline strategy based on our single-dose pharmacokinetic study.
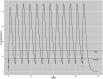
Study design: Six prematures received 60 mg/kg of L-citrulline every 6 hours for 72 hours. Plasma L-citrulline concentrations were measured before the first and last L-citrulline doses. L-citrulline concentrations were compared to concentration-time profiles from our previous study.
Results: Plasma L-citrulline concentrations agreed with the simulated concentration-time profiles. No serious adverse events occurred.
Conclusions: Simulations based on single-doses can be used to predict target multi-dose plasma L-citrulline concentrations. These results assist the design of RCTs evaluating the safety and effectiveness of L-citrulline therapy for BPD-PH. Clinical trials.gov ID: NCT03542812.
Keywords: L-arginine; nitric oxide; pharmacokinetics.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS: CDF and JLA are inventors on a patent at Vanderbilt University Medical Center that has been licensed to Asklepion Pharmaceuticals for the “Therapeutic treatment of bronchopulmonary dysplasia.”
Figures


References
-
- Levy PT, Levin J, Leeman KT, Mullen MP, Hansmann G, Kourembanas S. Diagnosis and management of pulmonary hypertension in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 2022, 27(4): 101351. - PubMed
Publication types
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

