This is a preprint.
Metformin reduces SARS-CoV-2 in a Phase 3 Randomized Placebo Controlled Clinical Trial
- PMID: 37333243
- PMCID: PMC10275003
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.06.06.23290989
Metformin reduces SARS-CoV-2 in a Phase 3 Randomized Placebo Controlled Clinical Trial
Abstract
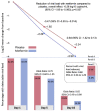
Current antiviral treatment options for SARS-CoV-2 infections are not available globally, cannot be used with many medications, and are limited to virus-specific targets.1-3 Biophysical modeling of SARS-CoV-2 replication predicted that protein translation is an especially attractive target for antiviral therapy.4 Literature review identified metformin, widely known as a treatment for diabetes, as a potential suppressor of protein translation via targeting of the host mTor pathway.5 In vitro, metformin has antiviral activity against RNA viruses including SARS-CoV-2.6,7 In the COVID-OUT phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of outpatient treatment of COVID-19, metformin had a 42% reduction in ER visits/hospitalizations/death through 14 days; a 58% reduction in hospitalizations/death through 28 days, and a 42% reduction in Long COVID through 10 months.8,9 Here we show viral load analysis of specimens collected in the COVID-OUT trial that the mean SARS-CoV-2 viral load was reduced 3.6-fold with metformin relative to placebo (-0.56 log10 copies/mL; 95%CI, -1.05 to -0.06, p=0.027) while there was no virologic effect for ivermectin or fluvoxamine vs placebo. The metformin effect was consistent across subgroups and with emerging data.10,11 Our results demonstrate, consistent with model predictions, that a safe, widely available,12 well-tolerated, and inexpensive oral medication, metformin, can be repurposed to significantly reduce SARS-CoV-2 viral load.
Figures
References
-
- Bramante C.T. B J.B., Liebovitz D. et al. Outpatient Treatment of Covid-19 and the Development of Long Covid over 10 Months: A Multi-Center, Quadruple-Blind, Parallel Group Randomized Phase 3 Trial. https://ssrncom/abstract=4375620 2023; - PMC - PubMed
-
- Castle BT, Dock C, Hemmat M, et al. Biophysical modeling of the SARS-CoV-2 viral cycle reveals ideal antiviral targets. bioRxiv. 2020:2020.05.22.111237. doi: 10.1101/2020.05.22.111237 - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
- K23 DK124654/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK048520/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002494/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 HL161847/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002489/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA210190/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL129956/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK124723/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 LM012744/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 HL156812/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM012982/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL133604/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR002492/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA254849/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
