This is a preprint.
Syk-dependent alternative homologous recombination activation promotes cancer resistance to DNA targeted therapy
- PMID: 37333340
- PMCID: PMC10275042
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2922520/v1
Syk-dependent alternative homologous recombination activation promotes cancer resistance to DNA targeted therapy
Update in
-
Syk-dependent homologous recombination activation promotes cancer resistance to DNA targeted therapy.Drug Resist Updat. 2024 May;74:101085. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2024.101085. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Drug Resist Updat. 2024. PMID: 38636338 Free PMC article.
Abstract
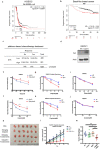
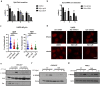
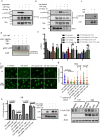
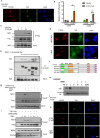
Enhanced DNA repair is an important mechanism of inherent and acquired resistance to DNA targeted therapies, including poly ADP ribose polymerase inhibition. Spleen associated tyrosine kinase (Syk) is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase known to regulate immune cell function, cell adhesion, and vascular development. Here, we report that Syk can be expressed in high grade serous ovarian cancer and triple negative breast cancers and promotes DNA double strand break resection, homologous recombination (HR) and therapeutic resistance. We found that Syk is activated by ATM following DNA damage and is recruited to DNA double strand breaks by NBS1. Once at the break site, Syk phosphorylates CtIP, a key mediator of resection and HR, at Thr-847 to promote repair activity, specifically in Syk expressing cancer cells. Syk inhibition or genetic deletion abolished CtIP Thr-847 phosphorylation and overcame the resistant phenotype. Collectively, our findings suggest that Syk drives therapeutic resistance by promoting DNA resection and HR through a novel ATM-Syk-CtIP pathway, and that Syk is a new tumor-specific target to sensitize Syk-expressing tumors to PARPi and other DNA targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

