This is a preprint.
Quorum-sensing agr system of Staphylococcus aureus primes gene expression for protection from lethal oxidative stress
- PMID: 37333372
- PMCID: PMC10274873
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.06.08.544038
Quorum-sensing agr system of Staphylococcus aureus primes gene expression for protection from lethal oxidative stress
Update in
-
Quorum-sensing agr system of Staphylococcus aureus primes gene expression for protection from lethal oxidative stress.Elife. 2024 Apr 30;12:RP89098. doi: 10.7554/eLife.89098. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38687677 Free PMC article.
Abstract
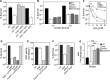
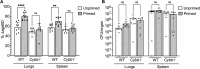
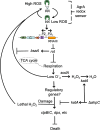
The agr quorum-sensing system links Staphylococcus aureus metabolism to virulence, in part by increasing bacterial survival during exposure to lethal concentrations of H2O2, a crucial host defense against S. aureus. We now report that protection by agr surprisingly extends beyond post-exponential growth to the exit from stationary phase when the agr system is no longer turned on. Thus, agr can be considered a constitutive protective factor. Deletion of agr increased both respiration and fermentation but decreased ATP levels and growth, suggesting that Δagr cells assume a hyperactive metabolic state in response to reduced metabolic efficiency. As expected from increased respiratory gene expression, reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulated more in the agr mutant than in wild-type cells, thereby explaining elevated susceptibility of Δagr strains to lethal H2O2 doses. Increased survival of wild-type agr cells during H2O2 exposure required sodA, which detoxifies superoxide. Additionally, pretreatment of S. aureus with respiration-reducing menadione protected Δagr cells from killing by H2O2. Thus, genetic deletion and pharmacologic experiments indicate that agr helps control endogenous ROS, thereby providing resilience against exogenous ROS. The long-lived "memory" of agr-mediated protection, which is uncoupled from agr activation kinetics, increased hematogenous dissemination to certain tissues during sepsis in ROS-producing, wild-type mice but not ROS-deficient (Nox2-/-) mice. These results demonstrate the importance of protection that anticipates impending ROS-mediated immune attack. The ubiquity of quorum sensing suggests that it protects many bacterial species from oxidative damage.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; agr; peroxide (H2O2); quorum-sensing; reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Conflict of interest statement
Potential competing interests. B.S. has consulted for Basilea Pharmaceutica. V.J.T. has received honoraria from Pfizer and MedImmune, and is an inventor on patents and patent applications filed by New York University, which are currently under commercial license to Janssen Biotech Inc. Janssen Biotech Inc. provides research funding and other payments associated with a licensing agreement. All other authors: no competing interests declared.
Figures







References
-
- Spaan AN, Surewaard BG, Nijland R, van Strijp JA. 2013. Neutrophils versus Staphylococcus aureus: a biological tug of war. Annu Rev Microbiol 67:629–650. - PubMed
-
- Drlica K, Zhao X. 2021. Bacterial death from treatment with fluoroquinolones and other lethal stressors. Expert review of anti-infective therapy 19:601–618. - PubMed
-
- Kohanski MA, Dwyer DJ, Hayete B, Lawrence CA, Collins JJ. 2007. A common mechanism of cellular death induced by bactericidal antibiotics. Cell 130:797–810. - PubMed
-
- Shatalin K, Nuthanakanti A, Kaushik A, Shishov D, Peselis A, Shamovsky I, Pani B, Lechpammer M, Vasilyev N, Shatalina E, Rebatchouk D, Mironov A, Fedichev P, Serganov A, Nudler E. 2021. Inhibitors of bacterial H(2)S biogenesis targeting antibiotic resistance and tolerance. Science 372:1169–1175. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
