The modular pYT vector series employed for chromosomal gene integration and expression to produce carbazoles and glycolipids in P. putida
- PMID: 37333445
- PMCID: PMC10117823
- DOI: 10.1093/femsmc/xtac030
The modular pYT vector series employed for chromosomal gene integration and expression to produce carbazoles and glycolipids in P. putida
Abstract
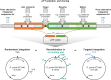
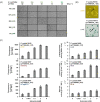
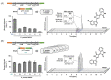
The expression of biosynthetic genes in bacterial hosts can enable access to high-value compounds, for which appropriate molecular genetic tools are essential. Therefore, we developed a toolbox of modular vectors, which facilitate chromosomal gene integration and expression in Pseudomonas putida KT2440. To this end, we designed an integrative sequence, allowing customisation regarding the modes of integration (random, at attTn7, or into the 16S rRNA gene), promoters, antibiotic resistance markers as well as fluorescent proteins and enzymes as transcription reporters. We thus established a toolbox of vectors carrying integrative sequences, designated as pYT series, of which we present 27 ready-to-use variants along with a set of strains equipped with unique 'landing pads' for directing a pYT interposon into one specific copy of the 16S rRNA gene. We used genes of the well-described violacein biosynthesis as reporter to showcase random Tn5-based chromosomal integration leading to constitutive expression and production of violacein and deoxyviolacein. Deoxyviolacein was likewise produced after gene integration into the 16S rRNA gene of rrn operons. Integration in the attTn7 site was used to characterise the suitability of different inducible promoters and successive strain development for the metabolically challenging production of mono-rhamnolipids. Finally, to establish arcyriaflavin A production in P. putida for the first time, we compared different integration and expression modes, revealing integration at attTn7 and expression with NagR/PnagAa to be most suitable. In summary, the new toolbox can be utilised for the rapid generation of various types of P. putida expression and production strains.
Keywords: Pseudomonas putida; carbazoles; chromosomal gene integration; glycolipids; synthetic biology; toolbox.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of FEMS.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rapid generation of recombinant Pseudomonas putida secondary metabolite producers using yTREX.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2017 Nov 15;2(4):310-319. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2017.11.001. eCollection 2017 Dec. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 29552656 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas putida rDNA is a favored site for the expression of biosynthetic genes.Sci Rep. 2019 May 7;9(1):7028. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43405-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31065014 Free PMC article.
-
Reliable Genomic Integration Sites in Pseudomonas putida Identified by Two-Dimensional Transcriptome Analysis.ACS Synth Biol. 2024 Jul 19;13(7):2060-2072. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.3c00747. Epub 2024 Jul 5. ACS Synth Biol. 2024. PMID: 38968167 Free PMC article.
-
Biofilm as a production platform for heterologous production of rhamnolipids by the non-pathogenic strain Pseudomonas putida KT2440.Microb Cell Fact. 2016 Oct 24;15(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s12934-016-0581-9. Microb Cell Fact. 2016. PMID: 27776509 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic tools for reliable gene expression and recombineering in Pseudomonas putida.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Jul;45(7):517-527. doi: 10.1007/s10295-017-2001-5. Epub 2018 Jan 3. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29299733 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Optimizing Systems for Robust Heterologous Production of Biosurfactants Rhamnolipid and Lyso-Ornithine Lipid in Pseudomonas putida KT2440.Molecules. 2024 Jul 11;29(14):3288. doi: 10.3390/molecules29143288. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39064867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alam K, Hao J, Zhang Yet al. . Synthetic biology-inspired strategies and tools for engineering of microbial natural product biosynthetic pathways. Biotechnol Adv. 2021;49:107759. - PubMed
-
- Antoine R, Locht C.. Isolation and molecular characterization of a novel broad-host-range plasmid from Bordetella bronchiseptica with sequence similarities to plasmids from Gram-positive organisms. Mol Microbiol. 1992;6:1785–99. - PubMed
-
- Bagdasarian M, Lurz R, Rückert Bet al. . Specific-purpose plasmid cloning vectors II. Broad host range, high copy number, RSF1010-derived vectors, and a host-vector system for gene cloning in Pseudomonas. Gene. 1981;16:237–47. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
