A Glance at Biogenesis and Functionality of MicroRNAs and Their Role in the Neuropathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 37333462
- PMCID: PMC10270766
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/7759053
A Glance at Biogenesis and Functionality of MicroRNAs and Their Role in the Neuropathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
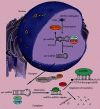
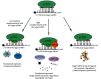
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short, noncoding RNA transcripts. Mammalian miRNA coding sequences are located in introns and exons of genes encoding various proteins. As the central nervous system is the largest source of miRNA transcripts in living organisms, miRNA molecules are an integral part of the regulation of epigenetic activity in physiological and pathological processes. Their activity depends on many proteins that act as processors, transporters, and chaperones. Many variants of Parkinson's disease have been directly linked to specific gene mutations which in pathological conditions are cumulated resulting in the progression of neurogenerative changes. These mutations can often coexist with specific miRNA dysregulation. Dysregulation of different extracellular miRNAs has been confirmed in many studies on the PD patients. It seems reasonable to conduct further research on the role of miRNAs in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease and their potential use in future therapies and diagnosis of the disease. This review presents the current state of knowledge about the biogenesis and functionality of miRNAs in the human genome and their role in the neuropathogenesis of Parkinson's disease (PD)-one of the most common neurodegenerative disorders. The article also describes the process of miRNA formation which can occur in two ways-the canonical and noncanonical one. However, the main focus was on miRNA's use in in vitro and in vivo studies in the context of pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of PD. Some issues, especially those regarding the usefulness of miRNAs in PD's diagnostics and especially its treatment, require further research. More standardization efforts and clinical trials on miRNAs are needed.
Copyright © 2023 Adam Szelągowski and Mariusz Kozakiewicz.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nikitina E. G., Urazova L. N., Stegny V. N. MicroRNAs and human cancer. Experimental oncology . 2012;34(1):2–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

