Nephroprotective Effects of Selenium Nanoparticles Against Sodium Arsenite-Induced Damages
- PMID: 37333733
- PMCID: PMC10276609
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S413362
Nephroprotective Effects of Selenium Nanoparticles Against Sodium Arsenite-Induced Damages
Abstract
Introduction: The potential effects of selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) administration on arsenic exposure-mediated nephrotoxicity by alleviating fibrosis, inflammation, oxidative stress-related damage, and apoptosis remains more detailed investigations.
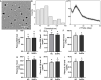
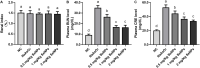
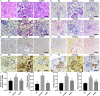
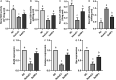
Methods: After the synthesis of selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) by sodium selenite (Na2SeO3) through a versatile and green procedure, the biosafety of SeNPs was assessed by assaying renal functions and inflammation in mice. Subsequently, nephroprotective effects of SeNPs against sodium arsenite (NaAsO2)-induced damages were confirmed by biochemical, molecular, and histopathological assays, including renal function, histological lesion, fibrosis, inflammation, oxidative stress-related damage, and apoptosis in mice renal tissues and renal tubular duct epithelial cells (HK2 cells).
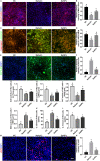
Results: The excellent biocompatibility and safety of SeNPs prepared in this study were confirmed by the non-significant differences in the renal functions and inflammation levels in mice between the negative control (NC) and 1 mg/kg SeNPs groups (p>0.05). The results of biochemical, molecular, and histopathological assays confirmed that daily administration of 1 mg/kg SeNPs for 4 weeks not only ameliorated renal dysfunctions and injuries caused by NaAsO2 exposure but also inhibited the fibrosis, inflammation, oxidative stress-related damage, and apoptosis in the renal tissues of NaAsO2-exposed mice. In addition, altered viability, inflammation, oxidative stress-related damage, and apoptosis in the NaAsO2-exposed HK2 cells were effectively reversed after 100 μg/mL SeNPs supplementation.
Conclusion: Our findings authentically confirmed the biosafety and nephroprotective effects of SeNPs against NaAsO2 exposure-induced damages by alleviating inflammation, oxidative stress-related damage, and apoptosis.
Keywords: apoptosis; arsenite; inflammation; nephroprotective; oxidative stress; selenium nanoparticles.
© 2023 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

