Estimation of Prostate Cancer Cost in Egypt From a Societal Perspective
- PMID: 37333760
- PMCID: PMC10275631
- DOI: 10.36401/JQSH-22-20
Estimation of Prostate Cancer Cost in Egypt From a Societal Perspective
Abstract
Introduction: The main objective of this study was to assess the cost of prostate cancer over a 1-year period from a societal perspective.
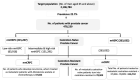
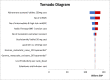
Methods: We constructed a cost-of-illness model to assess the cost of different health states of prostate cancer, metastatic or nonmetastatic, among Egyptian men. Population data and clinical parameters were extracted from the published literature. We relied on different clinical trials to extract clinical data. We considered all direct medical costs, including the costs of treatment and required monitoring, in addition to the indirect costs. The unit costs were captured from Nasr City Cancer Center and Egyptian Authority for Unified Procurement, Medical Supply, and Management of Medical Technology, and resource utilization were collected from clinical trials and validated by the Expert Panel. One-way sensitivity analysis was conducted to ensure model robustness.
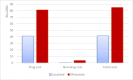
Results: The number of targeted patients with nonmetastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer, hormone-sensitive prostate cancer, and metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer was 215,207, 263,032, and 116,732, respectively. The total costs, in Egyptian pounds (EGP) and US dollars (USD), for the targeted patients, including drug costs and nondrug costs over a time horizon of 1 year, were EGP 41.44 billion (USD 9.010 billion) for localized prostate cancer; for metastatic prostate cancer, they doubled to EGP 85.14 billion (USD 18.510 billion), which reflects a huge burden on the Egyptian healthcare system. The drug costs for localized and metastatic prostate cancer are EGP 41,155,038,137 (USD 8.946 billion) and EGP 81,384,796,471 (USD 17.692 billion), respectively. A significant difference in nondrug costs between localized and metastatic prostate cancer was demonstrated. Nondrug costs were estimated at EGP 293,187,203 (USD 0.063 billion) for localized prostate cancer and EGP 3,762,286,092 (USD 0.817 billion) for metastatic prostate cancer. This significant difference in nondrug costs highlights the importance of early treatment due to the increased costs of progression and the burden of follow-up and productivity loss associated with metastatic prostate cancer.
Conclusion: Metastatic prostate cancer has a huge economic burden on the Egyptian healthcare system compared with localized prostate cancer owing to the increased costs of progression, follow-up, and productivity loss. This highlights the necessity of early treatment of these patients to save costs and lighten the burden of the disease on the patient, society, and economy.
Keywords: Egypt; cost of illness; economic burden; prostate cancer; societal perspective.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None.
Figures
References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Weiderpass E, Soerjomataram I. The ever-increasing importance of cancer as a leading cause of premature death worldwide. Cancer . 2021;127:3029–3030. - PubMed
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Caner J Clin . 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Xtandi (enzalutamide); FINOSE joint assessment report. FINOSE Joint HTA. 2018
-
- Egypt. International Agency for Research on Cancer World Health Organization. Accessed Oct 2021. gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/populations/818-egypt-fact-sheets.pdf.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
