Current progress in artificial intelligence-assisted medical image analysis for chronic kidney disease: A literature review
- PMID: 37333860
- PMCID: PMC10275698
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.05.029
Current progress in artificial intelligence-assisted medical image analysis for chronic kidney disease: A literature review
Abstract
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) causes irreversible damage to kidney structure and function. Arising from various etiologies, risk factors for CKD include hypertension and diabetes. With a progressively increasing global prevalence, CKD is an important public health problem worldwide. Medical imaging has become an important diagnostic tool for CKD through the non-invasive identification of macroscopic renal structural abnormalities. Artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted medical imaging techniques aid clinicians in the analysis of characteristics that cannot be easily discriminated by the naked eye, providing valuable information for the identification and management of CKD. Recent studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of AI-assisted medical image analysis as a clinical support tool using radiomics- and deep learning-based AI algorithms for improving the early detection, pathological assessment, and prognostic evaluation of various forms of CKD, including autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Herein, we provide an overview of the potential roles of AI-assisted medical image analysis for the diagnosis and management of CKD.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Chronic kidney disease; Deep learning; Radiomics.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, author- ship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

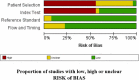
References
-
- Zhang L., Wang F., Wang L., et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in China: a cross-sectional survey. Lancet. 2012;379(9818):815–822. - PubMed
-
- Komenda P., Ferguson T.W., Macdonald K., et al. Cost-effectiveness of primary screening for CKD: a systematic review. Am J Kidney Dis: J Natl Kidney Found. 2014;63(5):789–797. - PubMed
-
- Kalantar-Zadeh K., Jafar T.H., Nitsch D., et al. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet. 2021;398(10302):786–802. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
