Early Draper-mediated glial refinement of neuropil architecture and synapse number in the Drosophila antennal lobe
- PMID: 37333889
- PMCID: PMC10272751
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1166199
Early Draper-mediated glial refinement of neuropil architecture and synapse number in the Drosophila antennal lobe
Abstract
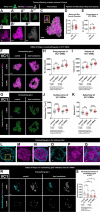
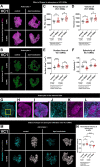
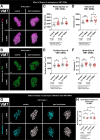
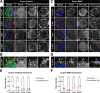
Glial phagocytic activity refines connectivity, though molecular mechanisms regulating this exquisitely sensitive process are incompletely defined. We developed the Drosophila antennal lobe as a model for identifying molecular mechanisms underlying glial refinement of neural circuits in the absence of injury. Antennal lobe organization is stereotyped and characterized by individual glomeruli comprised of unique olfactory receptor neuronal (ORN) populations. The antennal lobe interacts extensively with two glial subtypes: ensheathing glia wrap individual glomeruli, while astrocytes ramify considerably within them. Phagocytic roles for glia in the uninjured antennal lobe are largely unknown. Thus, we tested whether Draper regulates ORN terminal arbor size, shape, or presynaptic content in two representative glomeruli: VC1 and VM7. We find that glial Draper limits the size of individual glomeruli and restrains their presynaptic content. Moreover, glial refinement is apparent in young adults, a period of rapid terminal arbor and synapse growth, indicating that synapse addition and elimination occur simultaneously. Draper has been shown to be expressed in ensheathing glia; unexpectedly, we find it expressed at high levels in late pupal antennal lobe astrocytes. Surprisingly, Draper plays differential roles in ensheathing glia and astrocytes in VC1 and VM7. In VC1, ensheathing glial Draper plays a more significant role in shaping glomerular size and presynaptic content; while in VM7, astrocytic Draper plays the larger role. Together, these data indicate that astrocytes and ensheathing glia employ Draper to refine circuitry in the antennal lobe before the terminal arbors reach their mature form and argue for local heterogeneity of neuron-glia interactions.
Keywords: Draper; Drosophila; antennal lobe; critical period; glia; pruning; remodeling; synapse.
Copyright © 2023 Jindal, Leier, Salazar, Foden, Seitz, Wilkov, Coutinho-Budd and Broihier.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Becher P. G., Flick G., Rozpędowska E., Schmidt A., Hagman A., Lebreton S., et al. (2012). Yeast, not fruit volatiles mediate Drosophila melanogaster attraction, oviposition and development. Funct. Ecol. 26 822–828. 10.1111/j.1365-2435.2012.02006.x - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

