A multicenter phase II study on the safety of rho-kinase inhibitor (ripasudil) with needling for the patients after trabeculectomy
- PMID: 37333977
- PMCID: PMC10272279
- DOI: 10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101160
A multicenter phase II study on the safety of rho-kinase inhibitor (ripasudil) with needling for the patients after trabeculectomy
Abstract
Background: There is no established method of maintaining or reducing intra ocular pressure after the needling procedure for failing blebs post trabeculectomy. Regarding newer antihypertensive medications, ripasudil, which is a rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor ophthalmic solution, was able to prevent excessive scarring in vitro. This study aims to evaluate the safety of glaucoma patients submitted to the needling procedure and administered ripasudil for preventing scarring after the procedure. We also investigate the efficacy of ripasudil after needling for bleb failure through suppression of fibrosis to the bleb.
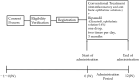
Methods: This study is a multicenter, open-label, single-arm, phase II trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of ripasudil in glaucoma patients after the needling procedure. Forty patients who will undergo needling at least 3 months after trabeculectomy will be recruited in Hiroshima university hospital and Hiroshima eye clinic. All the patients will instill ripasudil two times per day for three months after the needling procedure. The primary endpoint is the safety of ripasudil.
Conclusions: We plan to establish the safety of ripasudil and to collect information involving the efficacy of ripasudil widely in this study.
Keywords: A rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor; Glaucoma; Needling; Ripasudil; Trabeculectomy.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
-
- Quigley H.A., Addicks E.M., Green W.R., et al. Optic nerve damage in human glaucoma. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1981;99:635–649. - PubMed
-
- Cairns J.E. Trabeculectomy. Preliminary report of a new method. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1968;66:673–679. - PubMed
-
- Honjo M., Tanihara H., Kameda T., et al. Potential role of rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor Y-27632 in glaucoma filtration surgery. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007;48:5549–5557. - PubMed
-
- Cantor L.B., Mantravadi A., WuDunn D., et al. Morphologic classification of filtering blebs after glaucoma filtration surgery: the Indiana bleb appearance grading scale. J. Glaucoma. 2003;12:266–271. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources