Symptom Burden, Health Status, and Productivity in Patients with Uncontrolled and Controlled Severe Asthma in NOVELTY
- PMID: 37334017
- PMCID: PMC10274410
- DOI: 10.2147/JAA.S401445
Symptom Burden, Health Status, and Productivity in Patients with Uncontrolled and Controlled Severe Asthma in NOVELTY
Abstract
Background: Few studies have quantified symptom burden, health status, and productivity in patients with uncontrolled and controlled severe asthma. Up-to-date, real-world, global evidence is needed.
Objective: To quantify symptom burden, health status, and productivity in patients with uncontrolled and controlled severe asthma using baseline data from the NOVEL observational longiTudinal studY (NOVELTY; NCT02760329).
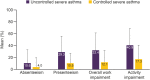
Methods: NOVELTY included patients aged ≥18 years (or ≥12 years in some countries) from primary care and specialist centres in 19 countries, with a physician-assigned diagnosis of asthma, asthma+chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or COPD. Disease severity was physician-assessed. Uncontrolled severe asthma was defined by an Asthma Control Test (ACT) score <20 and/or severe physician-reported exacerbations in the previous year; controlled severe asthma required an ACT score ≥20 and no severe exacerbations. Assessment of symptom burden included Respiratory Symptoms Questionnaire (RSQ) and ACT score. Assessment of health status included St George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ), EuroQoL 5 Dimensions 5 Levels Health Questionnaire (EQ-5D-5L) index value, and EQ-5D-5L Visual Analog Score (EQ-VAS). Assessment of productivity loss included absenteeism, presenteeism, overall work impairment, and activity impairment.
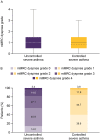
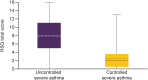
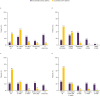
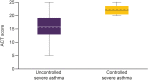
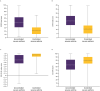
Results: Of 1652 patients with severe asthma, asthma was uncontrolled in 1078 (65.3%; mean age 52.6 years, 65.8% female) and controlled in 315 (19.1%; mean age 55.2 years, 56.5% female). With uncontrolled versus controlled severe asthma, symptom burden was higher (mean RSQ score 7.7 vs 2.5), health status more impaired (mean SGRQ total score 47.5 vs 22.4; mean EQ-5D-5L index value 0.68 vs 0.90; mean EQ-VAS score 64.1 vs 78.1), and productivity lower (presenteeism 29.3% vs 10.5%).
Conclusion: Our findings highlight the symptom burden of uncontrolled severe asthma compared with controlled severe asthma and its impact on patient health status and productivity, and support the need for interventions to improve control of severe asthma.
Keywords: asthma control; health status; productivity; symptom burden; symptom control; uncontrolled severe asthma.
© 2023 Ding et al.
Conflict of interest statement
B Ding is an employee of AstraZeneca. S Chen is an employee and shareholder of AstraZeneca. D Srivastava is a former employee of ZS Associates. A Quinton is an employee and shareholder of AstraZeneca. W Cook is an employee of AstraZeneca. A Papi has received research grants from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Teva; consulting fees from AstraZeneca, Avillion, Chiesi, Elpen Pharmaceuticals, GlaxoSmithKline, IQVIA, Novartis, and Sanofi; and payment or honoraria from AstraZeneca, Avillion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, Edmond Pharma, Elpen Pharmaceuticals, GlaxoSmithKline, IQVIA, Menarini, MSD, Mundipharma, Novartis, Sanofi, Teva, and Zambon; payments to his institution from Agenzia Italiana del farmaco (AIFA), AstraZeneca, Chiesi, GlaxoSmithKline and Sanofi. HK Reddel has participated in advisory boards for AstraZeneca, Chiesi, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, and Sanofi-Genzyme; has received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, Getz, GlaxoSmithKline, Sanofi, and Teva Pharmaceuticals for independent medical educational presentations; received independent research funding from AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, and Novartis; and received consulting fees from AstraZeneca and Novartis. She is Chair of the Global Institute for Asthma Science Committee and a member of the Australian National Asthma Council Guidelines Committee.
Figures

References
-
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention; 2022. Available from: https://ginasthma.org/reports/. Accessed 30, June, 2022.
-
- Dolan CM, Fraher KE, Bleecker ER, et al. Design and baseline characteristics of the epidemiology and natural history of asthma: outcomes and Treatment Regimens (TENOR) study: a large cohort of patients with severe or difficult-to-treat asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2004;92(1):32–39. doi:10.1016/S1081-1206(10)61707-3 - DOI - PubMed

