Remimazolam versus propofol for procedural sedation: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 37334113
- PMCID: PMC10269568
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.15495
Remimazolam versus propofol for procedural sedation: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: To improve patient tolerability and satisfaction as well as minimize complications, procedural sedation has been widely used. Propofol is the most widely used agent for induction of anesthesia and sedation by anesthesiologists. With a different mechanism compared to propofol, remimazolam is a new short-acting GABA-A receptor agonist. It is an ester-based benzodiazepine. This meta-analysis aims to clarify the efficacy and safety of remimazolam versus propofol for procedure sedation.
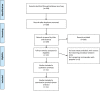
Methods: Electronic databases were searched for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing efficacy or safety of remimazolam versus propofol. Meta-analysis were conducted using RStudio with "metafor" package with random-effects model.
Results: A total of twelve RCTs were included in the meta-analysis. The pooled results demonstrated that patients with remimazolam for procedural sedation had lower risk of bradycardia (OR 0.28, 95% CI [0.14-0.57]), hypotension (OR 0.26, 95% CI [0.22-0.32]), and respiratory depression (OR 0.22, 95% CI [0.14-0.36]). There was no difference in the risk of developing postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) (OR 0.65, 95% CI [0.15-2.79]) and dizziness (OR 0.93, 95% CI [0.53-1.61]) between the remimazolam and propofol groups. Using remimazolam for procedural sedation is significantly associated with less injection pain compared to propofol (OR 0.06, 95% CI [0.03-0.13]). Regarding the sedation efficacy, there was no difference in sedation success rate or time to loss of consciousness, recover and discharge between the remimazolam and the propofol groups.
Conclusions: Based on our meta-analysis, patients receiving procedural sedation with remimazolam had lower risk of bradycardia, hypotension, respiratory depression and injection pain compared with propofol. On the other hand, there was no difference in sedation success rate, risk of PONV, dizziness, time to LOC, recovery and discharge between these two sedatives.
Prospero registration number: CRD42022362950.
Keywords: Meta-analysis; Procedural sedation; Propofol; Remimazolam.
©2023 Chang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Remimazolam versus propofol for procedural sedation and anesthesia: a systemic review and meta-analysis.Minerva Anestesiol. 2022 Dec;88(12):1035-1042. doi: 10.23736/S0375-9393.22.16817-3. Epub 2022 Nov 3. Minerva Anestesiol. 2022. PMID: 36326772
-
Remimazolam versus propofol for endoscopy sedation in elderly patients: a systematic review, meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis.Minerva Anestesiol. 2024 Sep;90(9):775-784. doi: 10.23736/S0375-9393.24.18027-3. Epub 2024 May 22. Minerva Anestesiol. 2024. PMID: 38775443
-
Comparison of remimazolam and propofol about safety outcome indicators during general anesthesia in surgical patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Minerva Anestesiol. 2023 Jun;89(6):553-564. doi: 10.23736/S0375-9393.23.17034-9. Epub 2023 Feb 27. Minerva Anestesiol. 2023. PMID: 36852570
-
The safety of remimazolam versus propofol in gastroscopic sedation: a meta-analysis.BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 Jan 29;24(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12871-024-02422-y. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 38287259 Free PMC article.
-
Remimazolam versus propofol for deep sedation/anaesthesia in upper gastrointestinal endoscopy in elderly patients: A multicenter, randomized controlled trial.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022 Dec;47(12):2230-2236. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13797. Epub 2022 Nov 5. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022. PMID: 36334013 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Remimazolam-Flumazenil versus Propofol for Recovery from General Anesthesia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2023 Nov 26;12(23):7316. doi: 10.3390/jcm12237316. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38068368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Remimazolam for Procedural Sedation in Older Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis with Trial Sequential Analysis.J Pers Med. 2024 Feb 29;14(3):276. doi: 10.3390/jpm14030276. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38541018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The 50% effective dose of remimazolam combined with different doses of esketamine for painless gastroscopy.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 14;15(1):12770. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97649-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40229355 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of remimazolam and propofol on delirium following anesthesia and sedation in elderly patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Anesthesiol. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):312. doi: 10.1186/s12871-025-03167-y. BMC Anesthesiol. 2025. PMID: 40597651 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating Remimazolam for Procedural Sedation.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2025;23(9):1009-1020. doi: 10.2174/011570159X367968250117034551. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39936418 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Benzoni T, Cascella M. StatPearls. Treasure Island StatPearls Publishing LLC: 2022. Procedural sedation. - PubMed
-
- Chen S, Wang J, Xu X, Huang Y, Xue S, Wu A, Jin X, Wang Q, Lyu J, Wang S, Li Y, Yu Y, Ai D, Luo A, Min S, Li L, Zou X, Liu J, Lv P, Chai X, Sun X, Zhao Z, Zhang J. The efficacy and safety of remimazolam tosylate versus propofol in patients undergoing colonoscopy: a multicentered, randomized, positive-controlled, phase III clinical trial. American Journal of Translational Research. 2020;12(8):4594–4603. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen SH, Yuan TM, Zhang J, Bai H, Tian M, Pan CX, Bao HG, Jin XJ, Ji FH, Zhong TD, Wang Q, Lv JR, Wang S, Li YJ, Yu YH, Luo AL, Li XK, Min S, Li L, Zou XH, Huang YG. Remimazolam tosilate in upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: a multicenter, randomized, non-inferiority, phase III trial. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2021;36(2):474–481. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15188. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

