Mechanosensitive Piezo1 protein as a novel regulator in macrophages and macrophage-mediated inflammatory diseases
- PMID: 37334369
- PMCID: PMC10275567
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1149336
Mechanosensitive Piezo1 protein as a novel regulator in macrophages and macrophage-mediated inflammatory diseases
Abstract
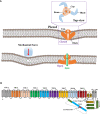
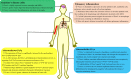
Macrophages are the most important innate immune cells in humans. They are almost ubiquitous in peripheral tissues with a large variety of different mechanical milieus. Therefore, it is not inconceivable that mechanical stimuli have effects on macrophages. Emerging as key molecular detectors of mechanical stress, the function of Piezo channels in macrophages is becoming attractive. In this review, we addressed the architecture, activation mechanisms, biological functions, and pharmacological regulation of the Piezo1 channel and review the research advancements in functions of Piezo1 channels in macrophages and macrophage-mediated inflammatory diseases as well as the potential mechanisms involved.
Keywords: Piezo1 channel; inflammatory diseases; macrophages; mechanical forces; mechanotransduction.
Copyright © 2023 Tang, Zhao, Zhuang, Zhong, Wang, Zhang and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanical gated ion channel Piezo1: Function, and role in macrophage inflammatory response.Innate Immun. 2024 Feb;30(2-4):32-39. doi: 10.1177/17534259241249287. Epub 2024 May 6. Innate Immun. 2024. PMID: 38710209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Piezo1 in chronic inflammatory diseases and prospects for drug treatment (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2025 Jul;32(1):200. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13565. Epub 2025 May 16. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 40376999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel in diseases.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2022 Aug;172:39-49. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2022.04.006. Epub 2022 Apr 15. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35436566 Review.
-
Piezo1 (Piezo-Type Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Component 1)-Mediated Mechanosensation in Macrophages Impairs Perfusion Recovery After Hindlimb Ischemia in Mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2023 Apr;43(4):504-518. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.122.318625. Epub 2023 Feb 9. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2023. PMID: 36756881
-
Mechanical force modulates macrophage proliferation via Piezo1-AKT-Cyclin D1 axis.FASEB J. 2022 Aug;36(8):e22423. doi: 10.1096/fj.202200314R. FASEB J. 2022. PMID: 35775626 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Piezo1 channels restrain ILC2s and regulate the development of airway hyperreactivity.J Exp Med. 2024 May 6;221(5):e20231835. doi: 10.1084/jem.20231835. Epub 2024 Mar 26. J Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38530239 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotropic physiological functions of Piezo1 in human body and its effect on malignant behavior of tumors.Front Physiol. 2024 Apr 16;15:1377329. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1377329. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38690080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of transient, constricted migration on neutrophil intracellular bacteria-killing capability.Immunity. 2024 Aug 13;57(8):1713-1715. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2024.07.008. Immunity. 2024. PMID: 39142267 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Shengyu decoction ameliorates knee osteoarthritis by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress via Piezo1 channels.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 14;16:1592818. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1592818. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40727099 Free PMC article.
-
Biological and clinical implications of a model of surveillance immunity.J Clin Invest. 2025 Aug 1;135(15):e191645. doi: 10.1172/JCI191645. eCollection 2025 Aug 1. J Clin Invest. 2025. PMID: 40759580 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blakney AK, Swartzlander MD, Bryant SJ. Student award winner in the undergraduate category for the society of biomaterials 9th world biomaterials congress, chengdu, China, June 1-5, 2012. J Biomed Materials Res Part A (2012) 100A:1375–86. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.34104 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

