Design, Synthesis, and Pharmacological Characterization of a Potent Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Acute Pancreatitis
- PMID: 37334504
- PMCID: PMC10350924
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00831
Design, Synthesis, and Pharmacological Characterization of a Potent Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Acute Pancreatitis
Abstract
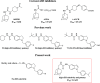
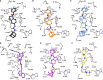
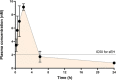
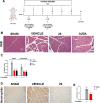
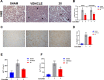
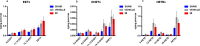
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a potentially life-threatening illness characterized by an exacerbated inflammatory response with limited options for pharmacological treatment. Here, we describe the rational development of a library of soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) inhibitors for the treatment of AP. Synthesized compounds were screened in vitro for their sEH inhibitory potency and selectivity, and the results were rationalized by means of molecular modeling studies. The most potent compounds were studied in vitro for their pharmacokinetic profile, where compound 28 emerged as a promising lead. In fact, compound 28 demonstrated a remarkable in vivo efficacy in reducing the inflammatory damage in cerulein-induced AP in mice. Targeted metabololipidomic analysis further substantiated sEH inhibition as a molecular mechanism of the compound underlying anti-AP activity in vivo. Finally, pharmacokinetic assessment demonstrated a suitable profile of 28 in vivo. Collectively, compound 28 displays strong effectiveness as sEH inhibitor with potential for pharmacological AP treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





References
-
- Trindade-da-Silva C. A.; Clemente-Napimoga J. T.; Abdalla H. B.; Rosa S. M.; Ueira-Vieira C.; Morisseau C.; Verri W. A.; Montalli V. A. M.; Hammock B. D.; Napimoga M. H. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor, TPPU, increases regulatory T cells pathway in an arthritis model. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 9074–9086. 10.1096/fj.202000415R. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Medical

