Comparative effectiveness of JAK inhibitors and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 37334513
- PMCID: PMC10338257
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2022.369
Comparative effectiveness of JAK inhibitors and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background/aims: We aimed to compare the effectiveness and safety of Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi) vs. biologic disease- modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARD) in Korean patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who had an inadequate response to conventional synthetic DMARDs.
Methods: A quasi-experimental, multi-center, prospective, non-randomized study was conducted to compare response rates between JAKi and bDMARDs in patients with RA naïve to targeted therapy. An interim analysis was performed to estimate the proportion of patients achieving low disease activity (LDA) based on disease activity score (DAS)-28- erythroid sedimentation rate (ESR) (DAS28-ESR) at 24 weeks after treatment initiation and to evaluate the development of adverse events (AEs).
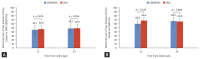
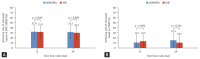
Results: Among 506 patients enrolled from 17 institutions between April 2020 and August 2022, 346 (196 JAKi group and 150 bDMARD group) were included in the analysis. After 24 weeks of treatment, 49.0% of JAKi users and 48.7% of bDMARD users achieved LDA (p = 0.954). DAS28-ESR remission rates were also comparable between JAKi and bDMARD users (30.1% and 31.3%, respectively; p = 0.806). The frequency of AEs reported in the JAKi group was numerically higher than that in the bDMARDs group, but the frequencies of serious and severe AEs were comparable between the groups.
Conclusion: Our interim findings reveal JAKi have comparable effectiveness and safety to bDMARDs at 24 weeks after treatment initiation.
Keywords: Comparative effectiveness research; Janus kinase inhibitor; Rheumatoid arthritis; Safety; Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no conflicts.
Figures


References
-
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Barton A, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:18001. - PubMed
-
- Burmester GR, Blanco R, Charles-Schoeman C, et al. ORAL Step investigators Tofacitinib (CP-690,550) in combination with methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis with an inadequate response to tumour necrosis factor inhibitors: a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2013;381:451–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
