Serine-arginine splicing factor 2 promotes oesophageal cancer progression by regulating alternative splicing of interferon regulatory factor 3
- PMID: 37335045
- PMCID: PMC10281462
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2023.2223939
Serine-arginine splicing factor 2 promotes oesophageal cancer progression by regulating alternative splicing of interferon regulatory factor 3
Abstract
Objective: Often, alternative splicing is used by cancer cells to produce or increase proteins that promote growth and survival through alternative splicing. Although RNA-binding proteins are known to regulate alternative splicing events associated with tumorigenesis, their role in oesophageal cancer (EC) has rarely been explored.
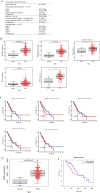
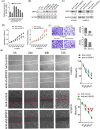
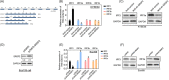
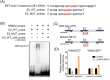
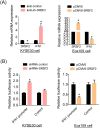
Methods: We analysed the expression pattern of several relatively well characterized splicing regulators on 183 samples from TCGA cohort of oesophageal cancer; the effectiveness of the knockdown of SRSF2 was subsequently verified by immunoblotting; we measured the ability of cells treated with lenti-sh-SRSF2/lenti-sh2-SRSF2 to invade through an extracellular matrix coating by transwell invasion assay; using RNA-seq data to identify its potential target genes; we performed qRT-PCR to detect the changes of exon 2 usage in lenti-sh-SRSF2 transduced KYSE30 cells to determine the possible effect of SRSF2 on splicing regulation of IRF3; RNA Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (RNA-EMSA) was performed by the incubation of purified SRSF2 protein and biotinylated RNA probes; we performed luciferase assay to confirm the effect of SRSF2 on IFN1 promoter activity.
Results: We found upregulation of SRSF2 is correlated with the development of EC; Knock-down of SRSF2 inhibits EC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion; SRSF2 regulates the splicing pattern of IRF3 in EC cells; SRSF2 interacts with exon 2 of IRF3 to regulate its exclusion; SRSF2 inhibits the transcription of IFN1 in EC cells.
Conclusion: This study identified a novel regulatory axis involved in EC from the various aspects of splicing regulation.
Keywords: IFN1; IRF3; SRSF2; alternative splicing; oesophageal cancer; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
