hucMSCs treatment prevents pulmonary fibrosis by reducing circANKRD42-YAP1-mediated mechanical stiffness
- PMID: 37335082
- PMCID: PMC10333056
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.204805
hucMSCs treatment prevents pulmonary fibrosis by reducing circANKRD42-YAP1-mediated mechanical stiffness
Abstract
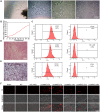
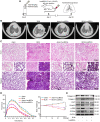
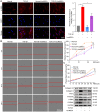
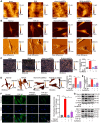
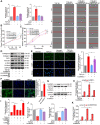
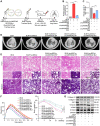
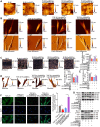
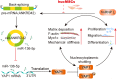
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a fibrosing interstitial pneumonia of unknown cause. The most typical characteristic of IPF is gradual weakening of pulmonary elasticity and increase in hardness/rigidity with aging. This study aims to identify a novel treatment approach for IPF and explore mechanism of mechanical stiffness underlying human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hucMSCs) therapy. Target ability of hucMSCs was examined by labeling with cell membrane dye Dil. Anti-pulmonary fibrosis effect of hucMSCs therapy by reducing mechanical stiffness was evaluated by lung function analysis and MicroCT imaging system and atomic force microscope in vivo and in vitro. Results showed that stiff environment of fibrogenesis caused cells to establish a mechanical connection between cytoplasm and nucleus, initiating expression of related mechanical genes such as Myo1c and F-actin. HucMSCs treatment blocked force transmission and reduced mechanical force. For further exploration of mechanism, ATGGAG was mutated to CTTGCG (the binding site of miR-136-5p) in the full-length sequence of circANKRD42. Wildtype and mutant plasmids of circANKRD42 were packaged into adenovirus vectors and sprayed into lungs of mice. Mechanistic dissection revealed that hucMSCs treatment repressed circANKRD42 reverse splicing biogenesis by inhibiting hnRNP L, which in turn promoted miR-136-5p binds to 3'-Untranslated Region (3'-UTR) of YAP1 mRNA directly, thus inhibiting translation of YAP1 and reducing YAP1 protein entering nucleus. The condition repressed expression of related mechanical genes to block force transmission and reduce mechanical forces. The mechanosensing mechanism mediated directly by circANKRD42-YAP1 axis in hucMSCs treatment, which has potential general applicability in IPF treatment.
Keywords: YAP1; circRNA; hucMSCs; mechanical stiffness; pulmonary fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

