PAX5 fusion genes in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A literature review
- PMID: 37335685
- PMCID: PMC10194640
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033836
PAX5 fusion genes in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A literature review
Abstract
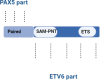
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a common cancer affecting children worldwide. The development of ALL is driven by several genes, some of which can be targeted for treatment by inhibiting gene fusions. PAX5 is frequently mutated in ALL and is involved in chromosomal rearrangements and translocations. Mutations in PAX5 interact with other genes, such as ETV6 and FOXP1, which influence B-cell development. PAX5/ETV6 has been observed in both B-ALL patients and a mouse model. The interaction between PAX5 and FOXP1 negatively suppresses the Pax5 gene in B-ALL patients. Additionally, ELN and PML genes have been found to fuse with PAX5, leading to adverse effects on B-cell differentiation. ELN-PAX5 interaction results in the decreased expression of LEF1, MB1, and BLNK, while PML-PAX5 is critical in the early stages of leukemia. PAX5 fusion genes prevent the transcription of the PAX5 gene, making it an essential target gene for the study of leukemia progression and the diagnosis of B-ALL.
Copyright © 2023 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. CureAll framework: WHO global initiative for childhood cancer: Increasing access, advancing quality, saving lives. 2021. Available at: https://apps.who.int/iris/rest/bitstreams/1385042/retrieve.
-
- American Cancer Society. Key statistics for acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL). 2023. Available at: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/acute-lymphocytic-leukemia/about/key-stati... [access date January 12, 2023].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

