Decreasing expression of HIF-1α, VEGF-A, and Ki67 with efficacy of neoadjuvant therapy in locally advanced cervical cancer
- PMID: 37335690
- PMCID: PMC10194672
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033820
Decreasing expression of HIF-1α, VEGF-A, and Ki67 with efficacy of neoadjuvant therapy in locally advanced cervical cancer
Abstract
Background: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) before radical hysterectomy has been widely used for locally advanced cervical cancer (LACC); However, its efficacy is yet to be determined.
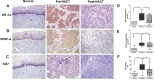
Methods: Effective and predictive biomarkers, which may aid in predicting the chemotherapy responses, were explored in this study. Initially, the expression of HIF-1α, VEGF-A, and Ki67 was detected in 42 paired (pre-NACT and post-NACT) LACC tissues, as well as 40 nonneoplastic cervical epithelial tissues by immunohistochemistry. Then, the correlation of the expression of HIF-1α, VEGF-A, Ki67 with the efficacy of NACT, as well as factors that affect the efficacy of NACT was analyzed.
Results: A clinical response occurred in 66.7% (28/42) of the patients, including 57.1% (16/28) with a complete response and 42.9% (12/28) with a partial response; While 33.33% (14/42) were non-responders, including 42.9% (6/14) with stable disease and 57.1% (8/14) with progressive disease. HIF-1α, VEGF-A, and Ki67 were overexpressed in LACC tissues compared to nonneoplastic tissues (P < .01, respectively); While the expression of HIF-1α, VEGF-A, and Ki67 was significantly decreased after NACT (P < .01, respectively). What's more, in the response group, HIF-1α, VEGF-A, and Ki67 expression were significantly decreased after chemotherapy in the post-chemotherapy cervical cancer tissues compared with the pre-chemotherapy cervical cancer tissues (all P < .05). Additionally, patients with lower histological grade and lower expression of HIF-1α, VEGF-A, and Ki67 were more responsive to NACT (P < .05, respectively); Moreover, the histological grade [P = .025, HR (95% CI): 0.133 (0.023-0.777)], HIF-1α [P = .019, HR (95% CI): 0.599 (0.390-0.918)], and Ki67 [P = .036, HR (95% CI): 0.946 (0898-0.996)] were independent risk factors affecting the efficacy of NACT in LACC.
Conclusion: Expression of HIF-1α, VEGF-A, and Ki67 were significantly decreased after NACT, and decreasing expression of HIF-1α, VEGF-A, and Ki67 were related to good response to NACT, suggesting HIF-1α, VEGF-A, and Ki67 may be implicated in evaluating the efficacy of NACT in LACC.
Copyright © 2023 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
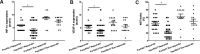
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Small W, Jr, Bacon MA, Bajaj A, et al. Cervical cancer: a global health crisis. Cancer. 2017;123:2404–12. - PubMed
-
- Gadducci A, Cosio S. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced cervical cancer: review of the literature and perspectives of clinical research. Anticancer Res. 2020;40:4819–28. - PubMed
-
- National Cancer Institute. Concurrent Chemoradiation for Cervical Cancer. Clinical Announcement. Washington DC: NCI; 1999.
-
- Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Locally Advanced Cervical Cancer Meta-analysis Collaboration. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced cervical cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data from 21 randomised trials. Eur J Cancer. 2003;39:2470–86. - PubMed

