Intraoperative MRI-Guided Resection Is Not Superior to 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Guidance in Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma: A Prospective Controlled Multicenter Clinical Trial
- PMID: 37335962
- PMCID: PMC10730068
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.22.01862
Intraoperative MRI-Guided Resection Is Not Superior to 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Guidance in Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma: A Prospective Controlled Multicenter Clinical Trial
Abstract
Purpose: Prospective data suggested a superiority of intraoperative MRI (iMRI) over 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) for achieving complete resections of contrast enhancement in glioblastoma surgery. We investigated this hypothesis in a prospective clinical trial and correlated residual disease volumes with clinical outcome in newly diagnosed glioblastoma.
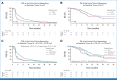
Methods: This is a prospective controlled multicenter parallel-group trial with two center-specific treatment arms (5-ALA and iMRI) and blinded evaluation. The primary end point was complete resection of contrast enhancement on early postoperative MRI. We assessed resectability and extent of resection by an independent blinded centralized review of preoperative and postoperative MRI with 1-mm slices. Secondary end points included progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS), patient-reported quality of life, and clinical parameters.
Results: We recruited 314 patients with newly diagnosed glioblastomas at 11 German centers. A total of 127 patients in the 5-ALA and 150 in the iMRI arm were analyzed in the as-treated analysis. Complete resections, defined as a residual tumor ≤0.175 cm³, were achieved in 90 patients (78%) in the 5-ALA and 115 (81%) in the iMRI arm (P = .79). Incision-suture times (P < .001) were significantly longer in the iMRI arm (316 v 215 [5-ALA] minutes). Median PFS and OS were comparable in both arms. The lack of any residual contrast enhancing tumor (0 cm³) was a significant favorable prognostic factor for PFS (P < .001) and OS (P = .048), especially in methylguanine-DNA-methyltransferase unmethylated tumors (P = .006).
Conclusion: We could not confirm superiority of iMRI over 5-ALA for achieving complete resections. Neurosurgical interventions in newly diagnosed glioblastoma shall aim for safe complete resections with 0 cm³ contrast-enhancing residual disease, as any other residual tumor volume is a negative predictor for PFS and OS.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02379572.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures



Comment in
-
Maximizing Extent of Resection for Noneloquent Glioblastoma: Fluorescent Dye or Intraoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging?J Clin Oncol. 2023 Dec 20;41(36):5493-5496. doi: 10.1200/JCO.23.00963. Epub 2023 Sep 18. J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37722089 No abstract available.
References
-
- Senft C, Bink A, Franz K, et al. : Intraoperative MRI guidance and extent of resection in glioma surgery: A randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 12:997-1003, 2011 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

