No Immunological Interference or Safety Concerns When Adjuvanted Recombinant Zoster Vaccine Is Coadministered With a Coronavirus Disease 2019 mRNA-1273 Booster Vaccine in Adults Aged 50 Years and Older: A Randomized Trial
- PMID: 37335963
- PMCID: PMC10640691
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciad361
No Immunological Interference or Safety Concerns When Adjuvanted Recombinant Zoster Vaccine Is Coadministered With a Coronavirus Disease 2019 mRNA-1273 Booster Vaccine in Adults Aged 50 Years and Older: A Randomized Trial
Abstract
Background: There is growing consensus that coronavirus disease 2019 booster vaccines may be coadministered with other age-appropriate vaccines. Adding to the limited available data supporting coadministration, especially with adjuvanted vaccines, could enhance vaccine coverage in adults.
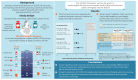
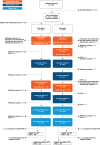
Methods: In this phase 3, randomized, open-label study, eligible adults aged ≥50 years were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive mRNA-1273 (50 µg) booster vaccination and a first dose of recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV1) 2 weeks apart (Seq group) or concomitantly (Coad group). The second RZV dose (RZV2) was administered 2 months post-RZV1 in both groups. Primary objectives were noninferiority of anti-glycoprotein E (gE) and anti-spike protein antibody responses in the Coad group compared to the Seq group. Safety and further immunogenicity assessments were secondary objectives.
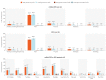
Results: In total, 273 participants were randomized to the Seq group and 272 to the Coad group. Protocol-specified noninferiority criteria were met. The adjusted geometric mean concentration ratio (Seq/Coad) was 1.01 (95% confidence interval [CI], .89-1.13) for anti-gE antibodies 1 month post-RZV2, and 1.09 (95% CI, .90-1.32) for anti-spike antibodies 1 month post-mRNA-1273 booster. No clinically relevant differences were observed in overall frequency, intensity, or duration of adverse events between the 2 study groups. Most solicited adverse events were mild/moderate in intensity, each with median duration ≤2.5 days. Administration site pain and myalgia were the most frequently reported in both groups.
Conclusions: Coadministration of mRNA-1273 booster vaccine with RZV in adults aged ≥50 years was immunologically noninferior to sequential administration and had a safety and reactogenicity profile consistent with both vaccines administered sequentially. Clinical Trials Registration. NCT05047770.
Keywords: coadministration; immunogenicity; mRNA COVID-19 vaccine; recombinant zoster vaccine; safety.
© GSK 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. A. N. is employed by GSK. A. K. is employed by GSK. P. P. is employed by GSK. J. D. is employed by GSK and holds shares in GSK. T. B. is employed by GSK and holds shares in GSK. A. M.-O. is employed by GSK and holds shares in GSK. B. L. is employed by Moderna and holds shares in Moderna. J. M. was employed by the GSK until May 2020 and is now employed by Moderna. J. M. also reports she holds shares in GSK and Moderna. K. A. is employed by Moderna and holds shares in Moderna. All authors declare no other financial and non-financial relationships and activities. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
No immunological interference or concerns about safety when seasonal quadrivalent influenza vaccine is co-administered with a COVID-19 mRNA-1273 booster vaccine in adults: A randomized trial.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024 Dec 31;20(1):2327736. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2327736. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024. PMID: 38513689 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Co-administration of the adjuvanted recombinant zoster vaccine with other adult vaccines: An overview.Vaccine. 2024 Mar 19;42(8):2026-2035. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2024.02.035. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Vaccine. 2024. PMID: 38423814 Review.
-
Immunogenicity and Safety of an Adjuvanted Herpes Zoster Subunit Vaccine Coadministered With Seasonal Influenza Vaccine in Adults Aged 50 Years or Older.J Infect Dis. 2017 Dec 12;216(11):1352-1361. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix481. J Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 29029224 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Immune response and safety of the adjuvanted recombinant zoster vaccine in adults 50 years of age and older in India: A randomized phase 3 trial.Vaccine. 2025 Mar 19;50:126819. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2025.126819. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Vaccine. 2025. PMID: 39923547 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety Profile of the Adjuvanted Recombinant Zoster Vaccine in Immunocompromised Populations: An Overview of Six Trials.Drug Saf. 2021 Jul;44(7):811-823. doi: 10.1007/s40264-021-01076-w. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Drug Saf. 2021. PMID: 34115324 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunogenicity of Recombinant Zoster Vaccine: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 May 11;12(5):527. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12050527. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38793778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety and Immunogenicity of Co-Administration of Herpes Zoster Vaccines with Other Vaccines in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Jun 12;13(6):637. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13060637. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40573968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
No immunological interference or concerns about safety when seasonal quadrivalent influenza vaccine is co-administered with a COVID-19 mRNA-1273 booster vaccine in adults: A randomized trial.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024 Dec 31;20(1):2327736. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2327736. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024. PMID: 38513689 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The safety of co-administration of recombinant zoster vaccine (Shingrix) and influenza vaccines in the elderly in VAERS during 2018-2024.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025 Dec;21(1):2525603. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2025.2525603. Epub 2025 Jul 11. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025. PMID: 40641250 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Immunogenicity, Efficacy, and Effectiveness of Recombinant Zoster Vaccine for Global Public Health Policy.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Feb 27;13(3):250. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13030250. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40266145 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Self WH, Tenforde MW, Rhoads JP, et al. Comparative effectiveness of Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech, and Janssen (Johnson & Johnson) vaccines in preventing COVID-19 hospitalizations among adults without immunocompromising conditions—United States, March–August 2021. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021; 70:1337–43. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Moderna COVID-19 vaccine standing orders for administering vaccine. 2022. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/covid-19/info-by-product/moderna/downloads/.... Accessed 25 October 2022.
-
- World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe . Interim recommendations on COVID-19 vaccination in autumn 2022 for the WHO European Region. In: European Technical Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization ad hoc virtual meeting, 5 July 2022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

